Figure 2.
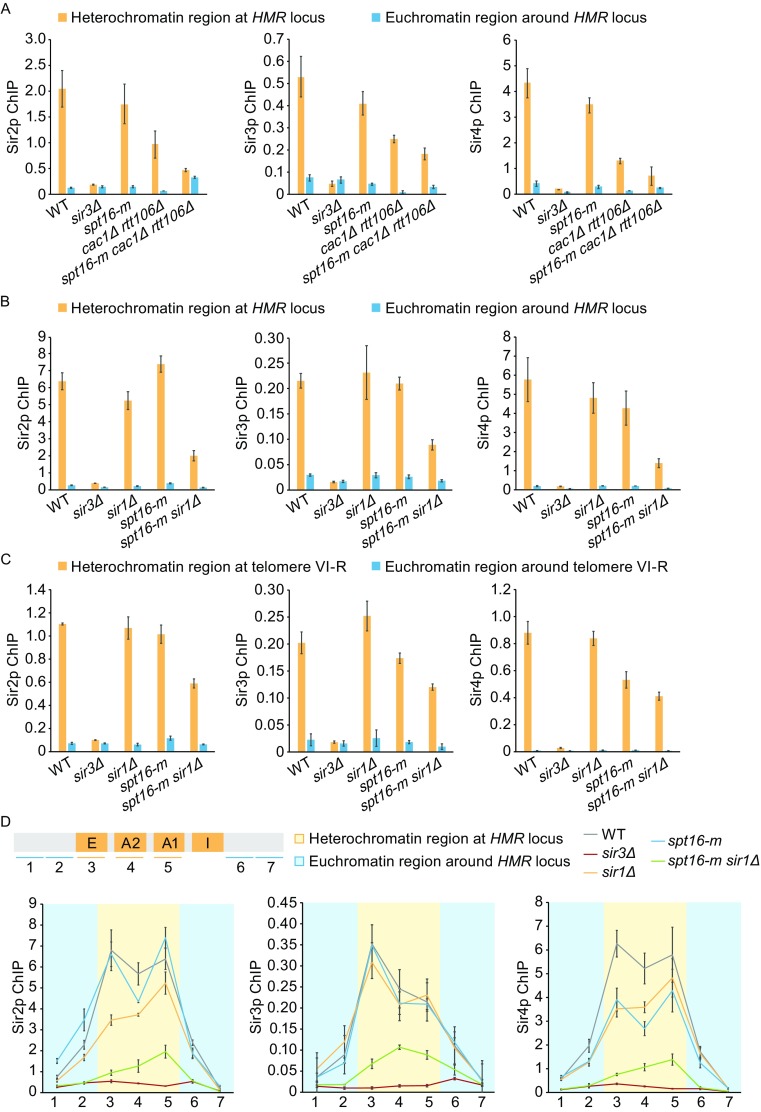
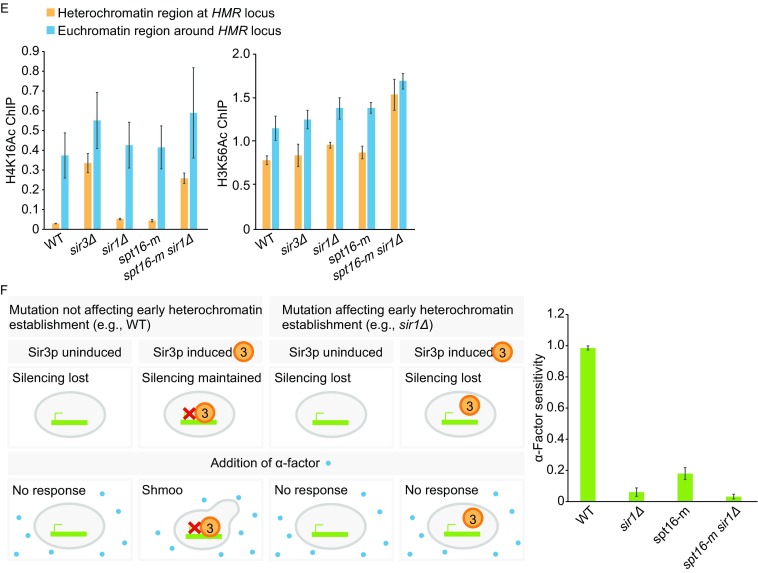
Spt16p is required for Sir2-4p binding to heterochromatin region and Spt16p cooperates with Sir1p during the establishment of heterochromatin silencing. (A) Sir2-4p binding at HMR locus is dramatically reduced in spt16-m cac1Δ rtt106Δ triple mutant cells. ChIP assays were performed using yeast strains of the indicated genotype and antibodies against Sir2p, Sir3p, and Sir4p, respectively. The error bars here represent SDs calculated from three technical repeats. The data are presented as the ratio of Sir proteins ChIP signal over input signal. sir3Δ strain was used as a control. (B and C) The association of Sir proteins to both HMR locus (B) and Chr VI-R telomeric region (C) is dramatically reduced in spt16-m sir1Δ double mutant cells. Sir2-4p ChIP was performed as described in (A). (D) The distribution pattern of Sir proteins at HMR locus has been changed in spt16-m sir1Δ double mutant cells. Top: A schematic diagram of HMR locus indicating the location of the primers used in this study. Bottom: The same ChIP assay was performed as described in (A) to map the distribution of Sir proteins across HMR locus in the indicated strains. (E) The level of H4K16Ac is increased at the heterochromatin region in spt16-m sir1Δ double mutant cells. ChIP assays were performed with antibodies against H4K16Ac and H3K56Ac. The data are presented as the ratio of H4K16Ac or H3K56Ac ChIP signal over input signal, with error bars indicating the SD for three technical repeats. (F) Spt16p has a role in the establishment of heterochromatin silencing. Left: A schematic diagram of the inducible heterochromatin establishment assay. There are two different mating types in S. cerevisiae: MATa and MATα. Selected strains for this assay are all MATa type cells, which normally only express a-specific genes and inhibit the expression of α-specific genes because of silencing at both HM loci. MATa cells will respond to the opposite mating pheromone, α-factor, by growing a protrusion called shmoo due to its distinct shape. In the absence of Sir3p (Sir3p uninduced), heterochromatin silencing is lost and such cells fail to respond to α-factor due to the expression of both a-specific and α-specific genes. This defect could be rescued by the induction of Sir3p if there are no other mutations except sir3Δ. In cells lacking Sir1p, a protein involved in heterochromatin establishment, establishment of silencing is affected. Green bar: HM loci; green arrow: the expression of α-specific genes; red cross: the inhibition of α-specific genes; orange circle with number 3: the presence of Sir3p; blue dot: α-factor. Right: The percentage of shmoo cells after Sir3p induction was counted (n = 3 with at least 200 cells for each genotype). Error bars: SDs calculated from three individual experiments
