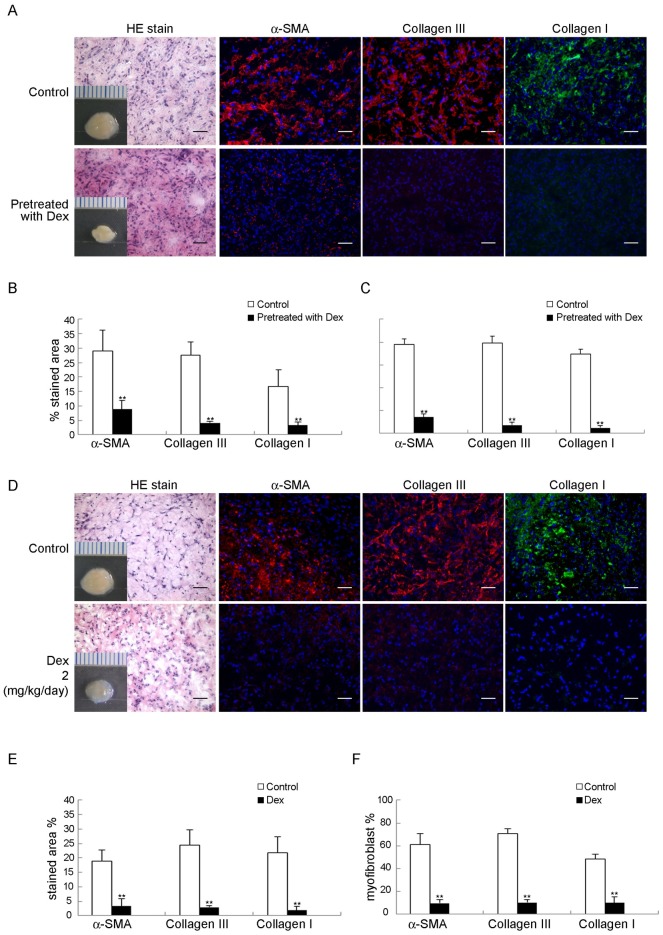
Fig 2. Dexamethasone inhibited FSCs formation of fibromatosis nodule in murine model.
(A–C) FSCs treated with 200 nM dexamethasone (Dex) for 3 days were then delivered with Matrigel, followed by transplantation beneath the dorsal skin of nude mice. (A) Macroscopic views of the transplants after 14 days in vivo. Scale = 1 mm. H&E staining and immunofluorescence staining for α-SMA, types III and type I collagen were performed. Bars = 50 μm. (B) The percentages of stained areas. (C) The percentages of myofibroblasts. (D–F) FSCs were delivered in Matrigel and transplanted under beneath the dorsal skin of nude mice. After 7 days, dexamethasone (2 mg/kg/day) dissolved in saline was injected subcutaneously daily for 1 week, and the control group received daily subcutaneous injections of 40 ml of saline alone for 1 week (D) Macroscopic views of the implants at 14 days of implantation in vivo. Scale = 1 mm. H&E staining and immunofluorescence staining for α-SMA, type III and type I collagen. Bars = 50 μm. (E) The percentages of stained areas. (F) The percentages of myofibroblasts. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). **, p<0.01 denotes statistical significance. All experiments were repeated with FSCs isolated from three different donors.