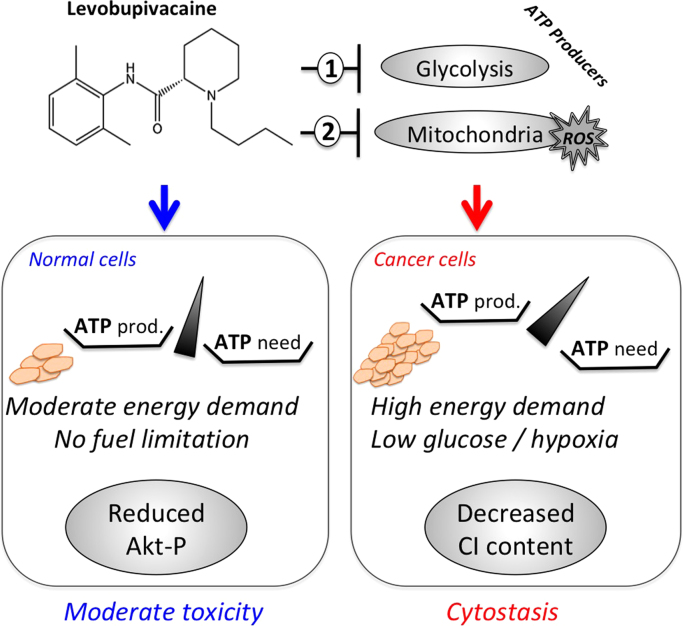
Fig. 6.
Bioenergetic and REDOX mechanism of levobupivacaine anti-cancer effect in prostate carcinoma (model). Levobupivacaine inhibits mitochondrial and glycolytic ATP level to specific extent, leading to a reduction of ATP level in the cell. Normal BHP cells respond by decreasing AKT survival pathway thereby triggering a moderate activation of apoptosis. Cancer cells with higher energy demand arrest proliferation and activate autophagy. Wortmannin blocks autophagy and potentializes levobupivacaine toxicity in cancer cells.