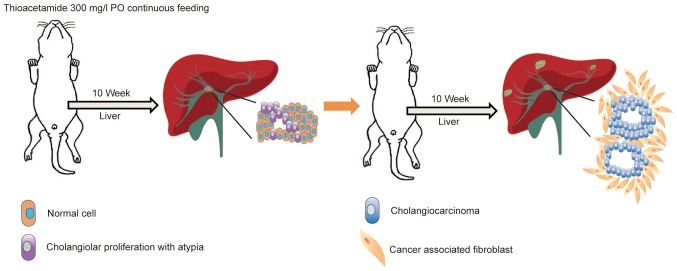
Figure 1.
Spontaneous TAA-induced IH-CCA model. The schematic diagram illustrates the administration of TAA to rats for 16 weeks for the development of spontaneous IH-CCA. TAA (300 mg/l) was continuously administered to rats by oral gavage. After 10 weeks of administration, the animals were sacrificed and cholangiolar viability with atypical ductal cells was evaluated in the liver tissues. Continuous feeding of the rats with TAA for a further 6 weeks results in the development of cholangiocarcinoma with surrounding cancer-associated fibroblasts. TAA, thioacetamide; IH-CCA, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.