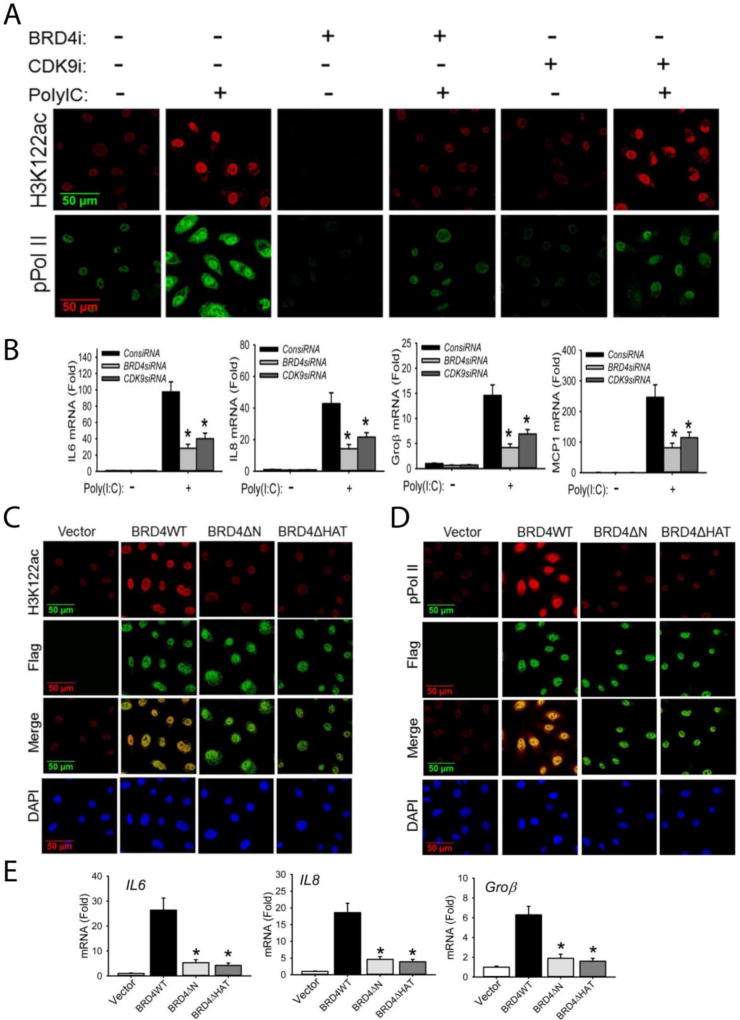
Figure 2. BRD4 is required for acetylation of H3K122 and cooperates with CDK9 for inducible phosphorylation of the RNA Pol II CTD.
(A). hSAECs were transfected with scrambled siRNA (control), BRD4-specific siRNA, or CDK9-specific siRNA (100 nM). 48 h later, cells were stimulated with extracellular poly(I:C) for 4 h. After fixation, cells were stained with anti-H3K122ac and anti-phospho-Ser 2 CTD RNA Pol II Abs as indicated. Secondary detection was Alexa 568-(red, for H3K122ac) and 488-(green, for pPol II) conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgGs. Images were acquired by confocal microscopy at 63× magnification. (B). Expression of IL6, IL8, Groβ, and MCP1 genes from the same experiment were quantified by Q-RT-PCR. Shown is the fold-change in mRNA abundance normalized to cyclophilin (PPIA). *: p < 0.01 compared to poly(I:C) only. Data are the means ± S.D. from n=3 experiments. (C). hSAECs were transfected with 4 µg pCMV2 empty vector (control), BRD4WT, BRD4 kinase mutant (BRD4ΔN) or BRD4 HAT mutant (BRD4ΔHAT) expression vectors. 24 h later, cells were fixed and stained with anti-H3K122 Ac rabbit Ab and anti-FLAG M2 mouse Ab. Secondary detection was Alexa 568-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (red, for H3K122ac) and 488-(green, for Flag) conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG respectively. Nuclei were counterstained and images acquired as in (A). (D). Transient transfectants were stained with anti-phospho-Ser 2 CTD RNA Pol II rabbit Ab and anti-FLAG M2 mouse Ab. Secondary detection, nuclear counterstaining and image acquisition are as in (C). (E).Expression of IL6, IL8, and Groβ were quantified by Q-RT-PCR. *: p < 0.01 compared to BRD4WT transfectants. Data are the means ± S.D. from n=3 experiments.