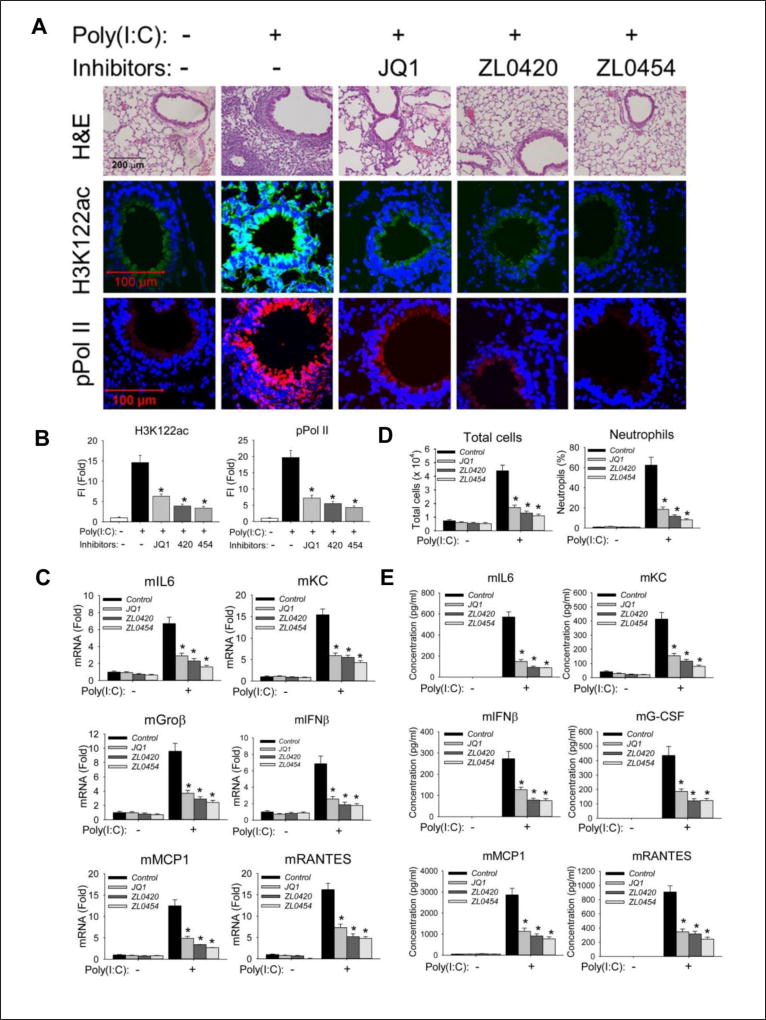
Figure 7. BRD4 inhibitors block poly(I:C) induced inflammation and neutrophilia in vivo.
C57BL6/J mice were pre-treated (IP) with ZL compounds before intranasal (IN) poly(I:C) exposure. (A). Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining (upper panel), immunofluorescence staining of H3K122ac (middle panel, in green color) and phospho-Ser 2 CTD RNA Pol II (lower panel, in red color) were performed on paraffin-embedded lung sections. (B). Quantifications of total fluorescence intensities of immunofluorescence staining of H3K122ac and phospho-Ser 2 CTD RNA Pol II. * p<0.01, n = 5. (C). Total lung RNA was isolated for measurement of mKC, mGroβ, mIL6, mIFNβ, mMCP1, and mRANTES mRNA abundance by Q-RT-PCR. m, mouse. *, p<0.01 compared to PBS only treated mice, n=5. (D). Total cells and neutrophils in the BALF, expressed as total number of cells X 104/ml (left) and percentage of neutrophils (right). (E). BALF cytokine abundance was measured using multiplex ELISA. *, p<0.01, n=5.