Table 1. Optimization of the sp3 C–H carbonylation a .
| ||||
| Entry | Oxidant | Base | Solvent | Yield b (%) |
| 1 | K2HPO4 | MeNO2 | 0 | |
| 2 | K2HPO4 | 1,4-Dioxane | 8 | |
| 3 | K2HPO4 | MeCN | Trace | |
| 4 | K2HPO4 | tBuOH | 11 | |
| 5 | K2HPO4 | tAmOH | 10 | |
| 6 | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | 14 | |
| 7 | O2 | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | Trace |
| 8 | AgOAc | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | Trace |
| 9 | (tBuO)2 | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | 18 |
| 10 | Na2S2O8 | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | 19 |
| 11 | K2S2O8 | K2HPO4 | iPrOH | 24 |
| 12 | K2S2O8 | Na2HPO4 | iPrOH | 26 |
| 13 | K2S2O8 | NaOAc | iPrOH | 31 |
| 14 | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH | 39 |
| 15 | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH/1,4-dioxane (0.45 : 0.55) | 54 |
| 16 c | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH/1,4-dioxane (0.45 : 0.55) | 65 |
| 17 c , d | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH/1,4-dioxane (0.45 : 0.55) | 71(68) |
| 18 c , d , e | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH/1,4-dioxane (0.45 : 0.55) | 0 |
| 19 c , d , f | K2S2O8 | PhCO2Na | iPrOH/1,4-dioxane (0.45 : 0.55) | 0 |
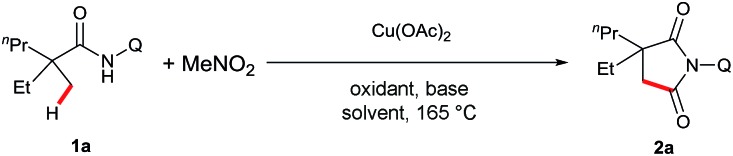
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.3 mmol), Cu(OAc)2 (1 eq.), oxidant (2 eq.), base (1 eq.), solvent (2 mL), 165 °C, 24 h.
bYields are based on 1a, determined by 1H NMR using dibromomethane as the internal standard. Isolated yield is in parenthesis.
cAl2O3 (60 mg).
dDMPU (2 eq.).
eNo MeNO2.
fNo Cu(OAc)2.
