Table 2. Optimization of the sp2 C–H carbonylation a .
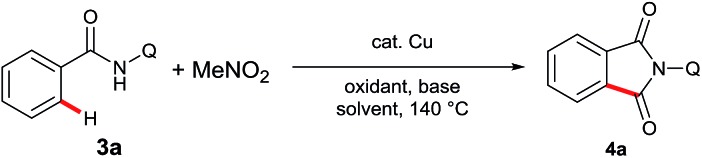
| |||||
| Entry | Cu source | Oxidant | Base | Solvent | Yield b (%) |
| 1 | Cu(OAc)2 | O2 | 1,4-Dioxane | 17 | |
| 2 | Cu(OAc)2 | MnO2 | 1,4-Dioxane | 28 | |
| 3 | Cu(OAc)2 | NMO | 1,4-Dioxane | 33 | |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2O | 1,4-Dioxane | 19 | |
| 5 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 | 1,4-Dioxane | 45 | |
| 6 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 | DMA | 74 | |
| 7 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 | PhCO2Na | DMA | 69 |
| 8 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 | Py | DMA | 86 |
| 9 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 | Na2HPO4 | DMA | 90(86) |
| 10 | CuCl | Ag2CO3 | Na2HPO4 | DMA | 76 |
| 11 | — | Ag2CO3 | Na2HPO4 | DMA | 0 |
aReaction conditions: 3a (0.3 mmol), Cu(OAc)2 (10 mol%), oxidant (2 eq.), base (1 eq.), solvent (2 mL), 140 °C, 24 h.
bYields are based on 3a, determined by 1H NMR using dibromomethane as the internal standard. Isolated yield is in parenthesis.
