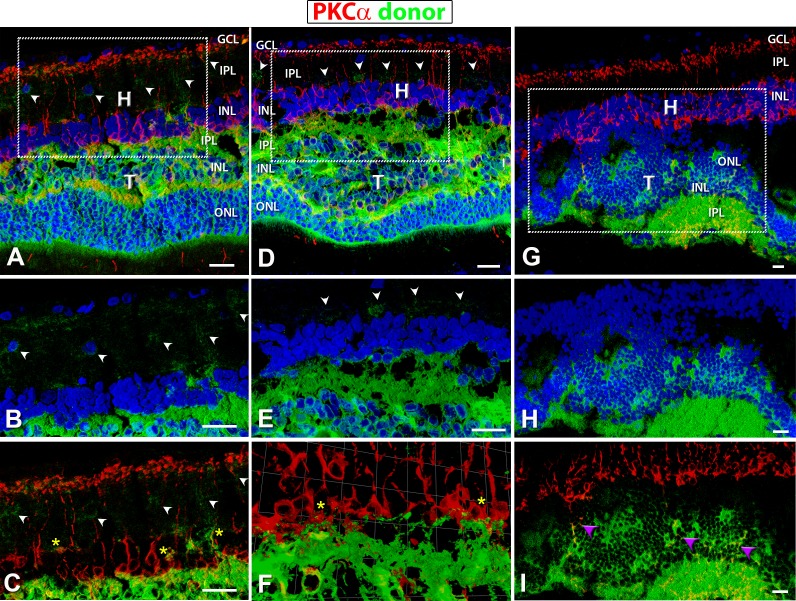
Figure 9.
hPAP (donor, green) and PKCα (red) staining in transplants. Protein kinase C α (PKC) (red: rod bipolar cells) labeling of transplanted eyes, donor tissue labeling with green (hPAP) and nuclei with blue (A–H; DAPI). (A–C) Well-laminated transplant no. 5 and (D–F) laminated transplant no. 6. (G–I) Upside-down transplant no. 1. (A, D, G) Overview images (all three channels). Boxes indicate areas of enlargements in (B, C, E, F, H, I). (B, E, H) hPAP staining (green) in combination with DAPI (blue); (E, F) PKCα (red) in combination with donor cell label (green). PKC labeling was found within the host as well as the transplant. Laminated transplants with many donor processes extending into the host retina (A–E) (white arrowheads) and wrapping around PKC-positive host bipolar cells (C, F) (yellow asterisks). (G–I) Transplant no. 1, partially upside-down and rosetted structure with no processes extending into host retina; but there were PKCα-positive cells within the transplant (purple arrowheads in [I]). Scale bars: 20 μm. H, host; T, transplant; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer.