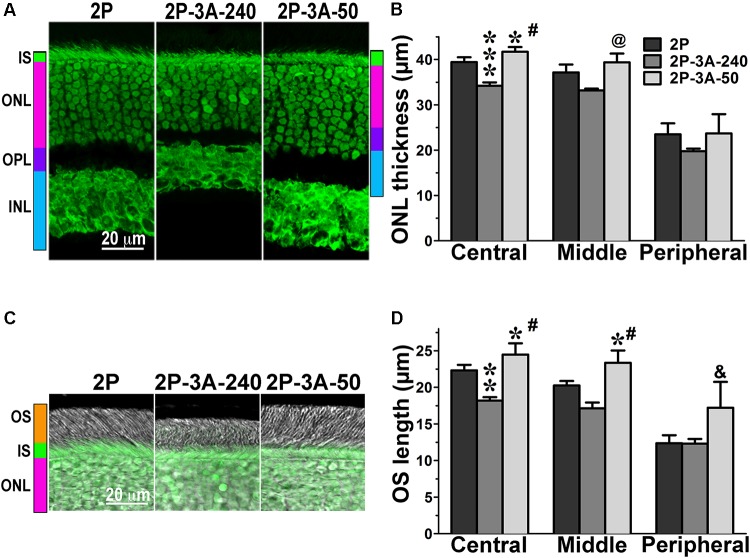
FIGURE 4.
The effect of enhanced arrestin-1-3A on photoreceptors expressing mutant rhodopsin with two phosphorylation sites. (A) Confocal green fluorescent Nissl images of the ONL in central retina sections of 5–6 weeks old mice expressing rhodopsin with two phosphorylation sites (2P) in the absence or presence of low (2P-3A-50) and high (2P-3A-240) levels of arrestin-1-3A mutant. The positions of outer segments (OS), inner segments (IS), outer nuclear layer (ONL), outer plexiform layer (OPL) and inner nuclear layer (INL) are shown on the left. (B) The thickness of the ONL (reflecting the number of rod photoreceptors) measured in the Central, Middle, and Peripheral retina were the average of inferior and superior retinal hemispheres. Means ± SE from three animals per genotype are shown. The comparison of the thickness of the ONL separately for each retinal subdivision by one-way ANOVA with Genotype as main factor revealed significant effect of Genotype for the Central (p < 0.0001) and Middle (p = 0.0075), but not Peripheral retina (p = 0.3997). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, as compared to 2P mice; #p < 0.001; @ p < 0.01 to the 3A-240 line by Bonferroni post hoc comparison. (C) Combined DIC and green fluorescent Nissl images of the retina sections of 5–6 weeks old mice of indicated genotypes, enlarged to show OS more clearly. The positions of the outer segments (OS), inner segments (IS), and outer nuclear layer (ONL) are shown on the left. (D) The length of the OS measured in the Central, Middle, and Peripheral retina were the average of inferior and superior retinal hemispheres. Means ± SE from three animals per genotype are shown. The length of OS was compared separately for each retinal subdivision by one-way ANOVA with Genotype as main factor, followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. The effect of Genotype was significant in all retinal subdivisions: the Central (p = 0.0003), Middle (0.0006), and Peripheral (0.027) retina. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, as compared to 2P animals; #p < 0.001; &p < 0.05 to the 3A-240 line by Bonferroni post hoc comparison.