Figure 6.
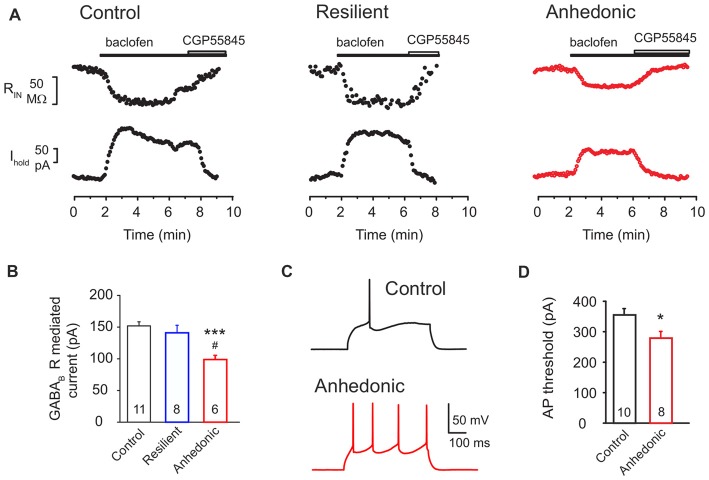
Postsynaptic GABAB receptor-mediated currents are reduced in the anhedonic rats. (A) Outward currents evoked by the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen (100 μM) in layer II–III pyramidal neurons (Vhold = −50 mV). The baclofen-induced current was associated with a reduced input resistance (RIN upper traces) and was reversed by the GABAB antagonist CGP55845 (8 μM). (B) Average GABABR mediated current was significantly reduced in pyramidal neurons of anhedonic rats (t-test: ***P < 0.001, vs. control; t-test #P < 0.05 vs. resilient). (C) Spiking elicited by current injection (350 pA/500 ms) in layer II–III pyramidal neurons from control (upper) and anhedonic rats (lower trace). Recordings were done in the presence of the ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist kynurenic acid (3 mM). (D) Average currents required to evoke an action potential (AP) in mPFC pyramidal neurons of control and anhedonic rats (t-test, *p < 0.05). The numbers of the recorded neurons are indicated in the columns.