Figure 2.
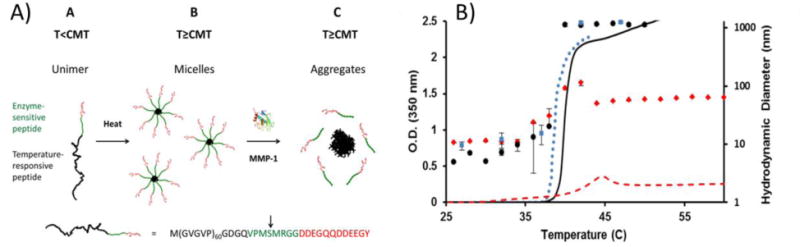
Micelle formation of a fusion protein consisting of elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) sequences, a matrix-metalloproteinase (MMP)-sensitive linker, and a hydrophilic domain. A) Upon heating, the protein formed micelles with an ELP core and a hydrophilic shell. When exposed to MMPs, the protein was cleaved and the ELP aggregated to form a coacervate phase. B) Change in aggregate size and solution opacity of ELP micelles. Optical density (lines) and hydrodynamic radius (individual data points) of MMP-sensitive ELP in the presence of MMP (black), MMP-sensitive ELP in the absence of MMP (red), and a negative control ELP without an MMP-sensitive linker or hydrophilic domain in the absence of MMP (blue). Reprinted (adapted) with permission from Analytical Chemistry, Simple Assay for Proteases Based on Aggregation of Stimulus-Responsive Polypeptides, 86, 2014, Ali Goorchian, Ashutosh Chilktoi, Gabriel P. Lopez. Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.
