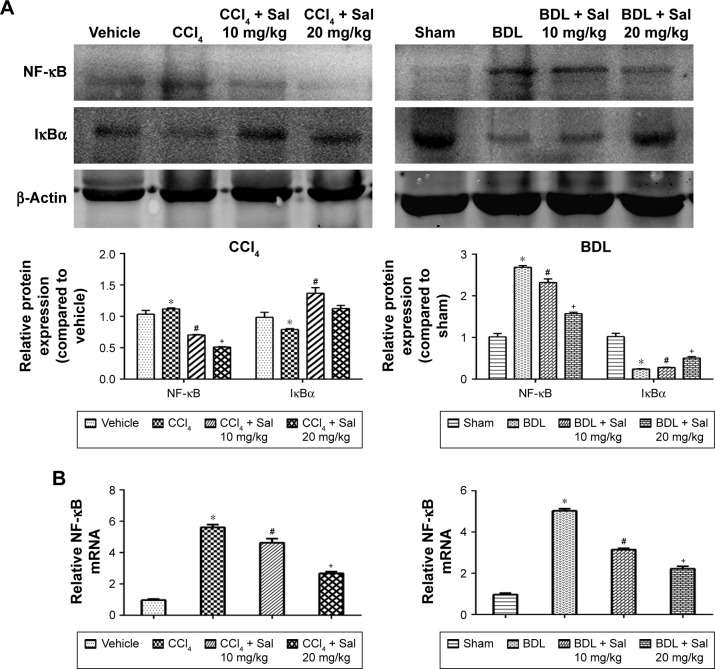
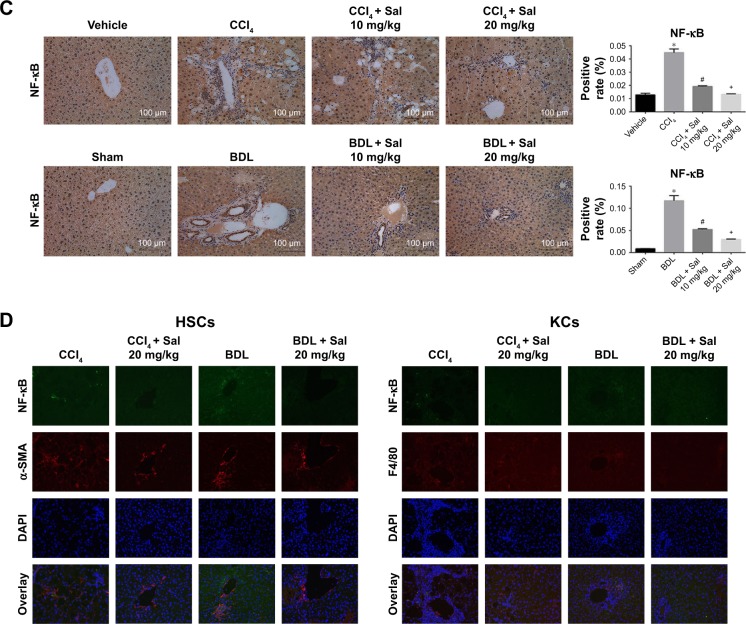
Figure 4.
Salidroside downregulated the NF-κB pathway in liver fibrosis.
Notes: (A) Western blot and quantitative analyses of NF-κB pathway. Salidroside inhibited NF-κB expression and increased IκBα expression in both mouse liver fibrosis models. (B) The qPCR analyses. Salidroside downregulated NF-κB mRNA expression levels. (C) Immunohistochemical staining showed that salidroside reduced the expression of NF-κB in liver tissues in both CCl4 and BDL groups (original magnification, ×200). (D) Representative images of double-immunofluorescence staining of liver sections were showed here (original magnification, ×400). α-SMA is considered to be a marker of activated HSCs, and F4/80 is the specific marker of KCs. There were positive areas in CCl4 and BDL groups. However, salidroside treatment could effectively inhibit the expression of NF-κB in these two kinds of cells. Data were given as mean ± SD (n=8, *P<0.05 for CCl4 or BDL group vs vehicle or sham group, #P<0.05 for CCl4 + Sal 10 mg/kg or BDL + Sal 10 mg/kg vs CCl4 or BDL group, and +P<0.05 for CCl4 + Sal 20 mg/kg or BDL + Sal 20 mg/kg vs CCl4 + Sal 10 mg/kg or BDL + Sal 10 mg/kg).
Abbreviations: BDL, bile duct ligation; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; KCs, Kupffer cells; qPCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; Sal, salidroside; SD, standard deviation.