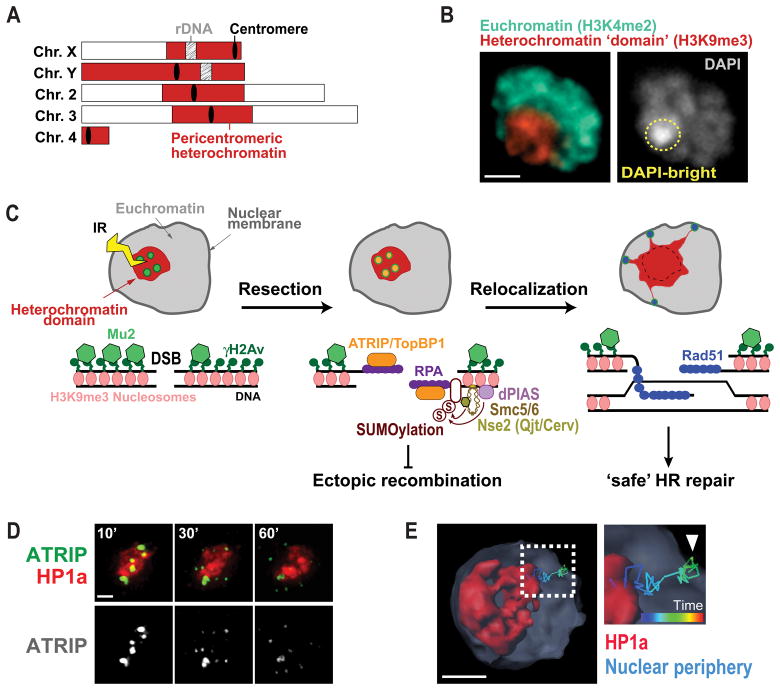
Figure 1. Nuclear dynamics of heterochromatin repair mechanisms in Drosophila cells.
A) Schematic view of Drosophila chromosomes showing the position and extent of pericentromeric heterochromatin. B) Immunofluorescence of a Kc cell showing heterochromatin organized as one distinct domain (red, H3K9me3) comprising the DAPI bright region (yellow circle). Euchromatin surrounds the heterochromatin domain (green, H3K4me2). Scale bar = 1μm. C) HR repair of heterochromatic DSBs starts inside the domain with H2Av phosphorylation and Mu2/Mdc1 recruitment. Resection also occur inside the domain resulting in ATRIP and TopBP1 foci. Next, the heterochromatin domain expands and repair foci relocalize to the nuclear periphery to form Rad51 foci and continue HR. dPIAS, Nse2/Qjt and Nse2/Cerv SUMO-ligases are required to block HR progression in the domain and prevent ectopic recombination. D) Live imaging of one Kc cell expressing mCh-HP1a and EGFP-ATRIP shows ATRIP foci inside the heterochromatin domain at 10 min after IR, which leave the domain by 60 min after IR (Chiolo et al., 2011). E) 4D reconstruction of one nucleus of a Kc cell expressing mCh-HP1a, mCh-LaminC and GFP-ATRIP, and exposed to IR, shows an example of a heterochromatic repair focus that leaves the heterochromatin domain and reaches the nuclear periphery (Ryu et al., 2015).