Figure 5. Image details in underexposed samples are recovered with post-image processing.
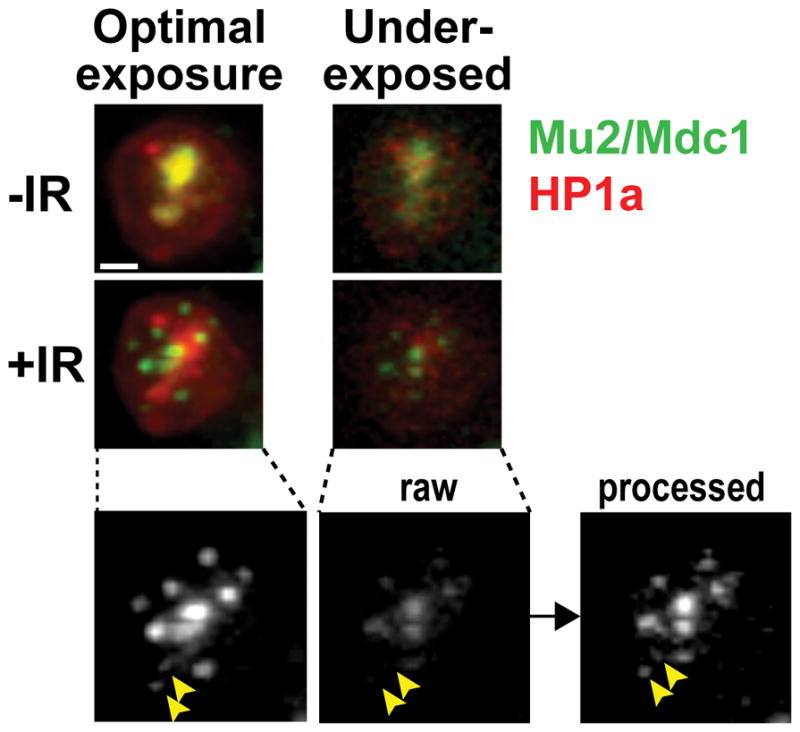
Underexposure of the cells enables the long and frequent image collection required for focus tracking while minimizing cell damage and photobleaching. The application of deconvolution and equalization algorithms enables recovery of most details in underexposed images. In the example shown, a Kc cell stably expressing mEGFP-Mu2 and mCh-HP1a shows an overall enrichment of Mu2/Mdc1 signals inside the heterochromatin domain before IR (-IR), and damage foci associated with the heterochromatin domain at 10 min after IR (+IR) (Ryu et al., 2015). The signal has been collected first in underexposed conditions (5 ms for mCh and 20 ms for GFP, with 10% T), then in optimal imaging conditions (12 ms for mCh and 20 ms for GFP, with 100% T), for both time points as indicated. The noisy signal of raw underexposed images is significantly improved by post-image processing (deconvolution and equalization), revealing even the weak signals associated with small foci (arrowheads). Images are max intensity projections of one nucleus. Scale bar = 1μm.
