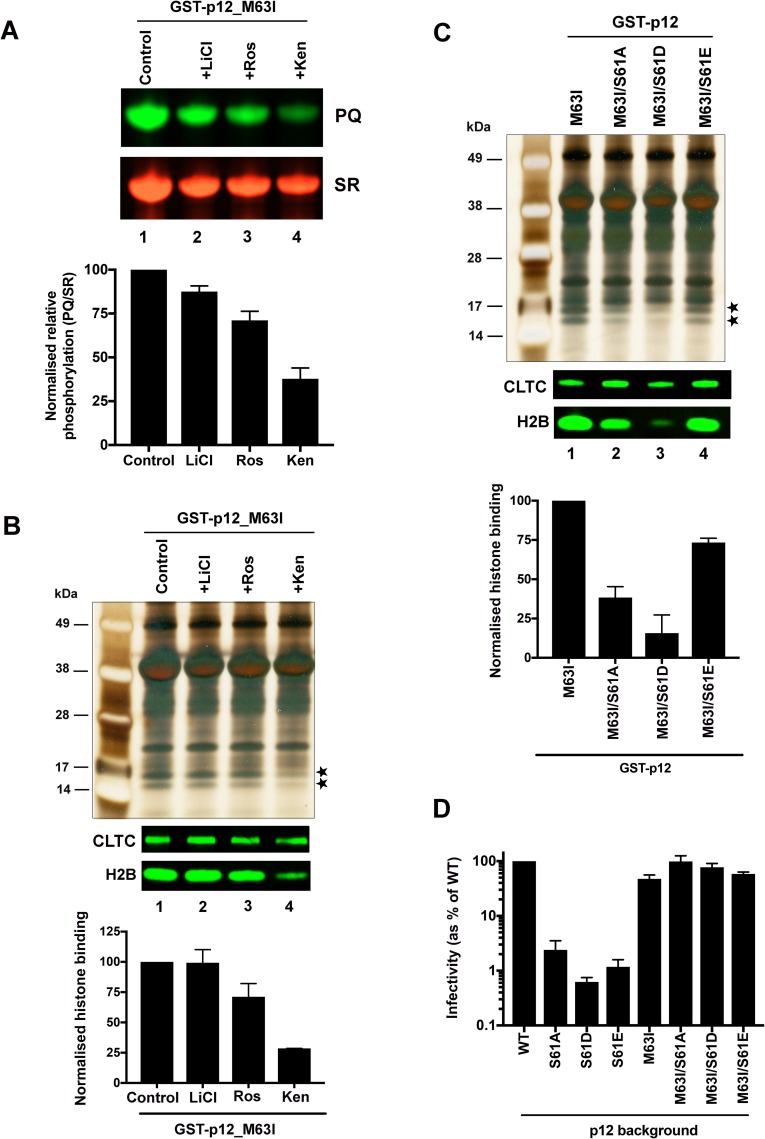
Fig 7. GST-tagged Mo-MLV p12_M63I has a higher affinity for chromatin when phosphorylated.
(A and B) The effect of kinase inhibitors on p12 phosphorylation (A) and chromatin association (B). 293T cells transiently-expressing GST-p12_M63I were treated overnight with nocodazole, followed by a kinase inhibitor (LiCl, roscovitine (Ros) or kenpaullone (Ken)) for 3.5 h in the presence of both nocodazole and MG132, before lysis. Normalised cell lysates were incubated with glutathione-sepharose beads, bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and gels were analysed either by sequential staining with ProQ diamond (PQ) and Sypro ruby (SR) dyes (A), or by silver-staining and immunoblotting with anti-CLTC and anti-H2B antibodies. PQ/SR ratios (A) and median H2B band intensities (B) are plotted in the bar charts as mean ± SD, of three technical replicates. (C) Mitotic chromatin association of GST-p12_M63I, S61 double mutants. 293T cells transiently-expressing GST-p12_M63I +/- an S61 mutation (S61A, S61D or S61E), were treated overnight with nocodazole and analysed as in (B). (D) Infectivity of Mo-MLV VLPs carrying alterations in p12. HeLa cells were challenged with equivalent RT units of LacZ-encoding VLPs carrying Mo-MLV p12_WT or M63I, +/- S61 mutations (S61A, S61D or S61E), and infectivity was measured 72 h post-infection by detection of beta-galactosidase activity in a chemiluminescent reporter assay. The data are plotted as percentage of WT VLP infectivity (mean ± SEM of >3 biological replicates).