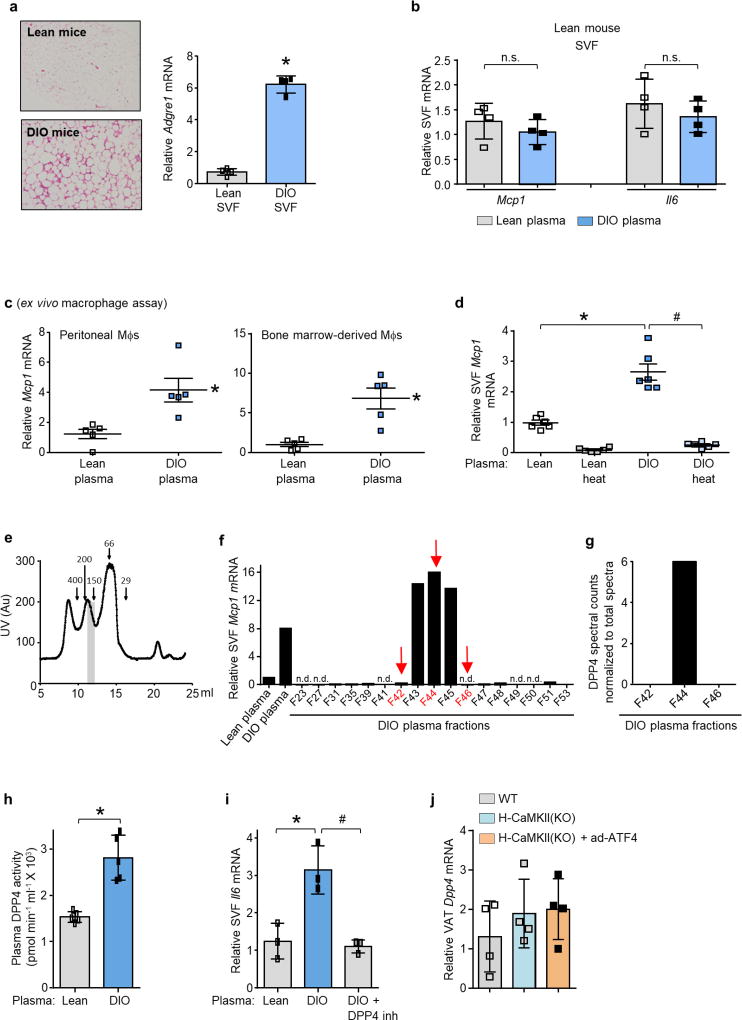
Extended Data Figure 2. DPP4 in the plasma of DIO mice induces Mcp1 and Il6 in SVF cells from the VAT of obese mice and in macrophages.
a, Representative images of haemotoxylin and eosin-stained VAT sections from lean and DIO mice and Adgre1 mRNA levels in SVF from lean and DIO mice. n = 4 mice per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05. b, SVF cells from the VAT of lean mice were incubated for 4 h in medium containing 10% (v/v) plasma from lean or DIO mice and then assayed for Mcp1 and Il6 mRNA. n = 4 mice per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05; n.s., not significant. c, Mcp1 mRNA was assayed in mouse peritoneal macrophages (Mφs) or bone marrow-derived macrophages that were incubated for 4 h with medium containing 10% (v/v) plasma from lean or DIO mice. n = 5 technical replicates per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05. d, Mcp1 mRNA levels in SVF cells that were incubated for 4 h with medium containing 10% (v/v) control or heat-inactivated (heat) plasma from the indicated groups of mice. n = 6 mice per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05. e, UV protein chromatogram obtained after fractionation of DIO mice plasma using gel-filtration FPLC; vertical grey bar depicts peak of activity shown in f. f, Obese mouse SVF cells were incubated with medium containing 10% lean or DIO mouse plasma or the indicated FPLC fractions from e and assayed for Mcp1 mRNA. n.d., Mcp1 mRNA not detected. Arrows indicate the fractions that were selected for LC–MS/MS analysis. g, LC–MS/MS normalized spectral counts corresponding to DPP4 in the FPLC fractions from f. h, DPP4 activity in the plasma of lean and DIO mice. n = 5 mice per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05. i, SVF cells from DIO mice were incubated for 4 h with medium containing 10% (v/v) lean or DIO mouse plasma that was pre-treated for 1 h with or without 10 µM DPP4 inhibitor KR62436. The cells were then assayed for Il6 mRNA. n = 3 technical replicates per group; mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05. j, VAT from the mice in Extended Data Fig. 1f, g was assayed for Dpp4 mRNA (n = 4). Data in a–c and h were analysed by two-tailed Student’s t-test; data in i and j were analysed by one-way ANOVA (g, h); data in d were analysed by two-way ANOVA.