Figure 2. AZD1480 induces apoptotic death of prostate cancer cells.
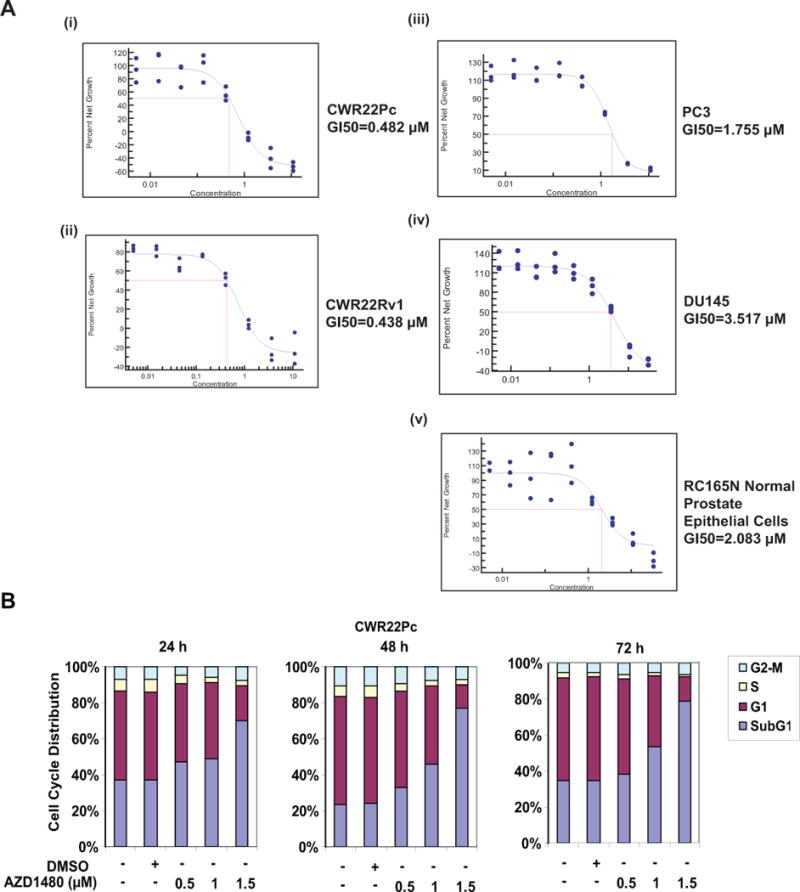
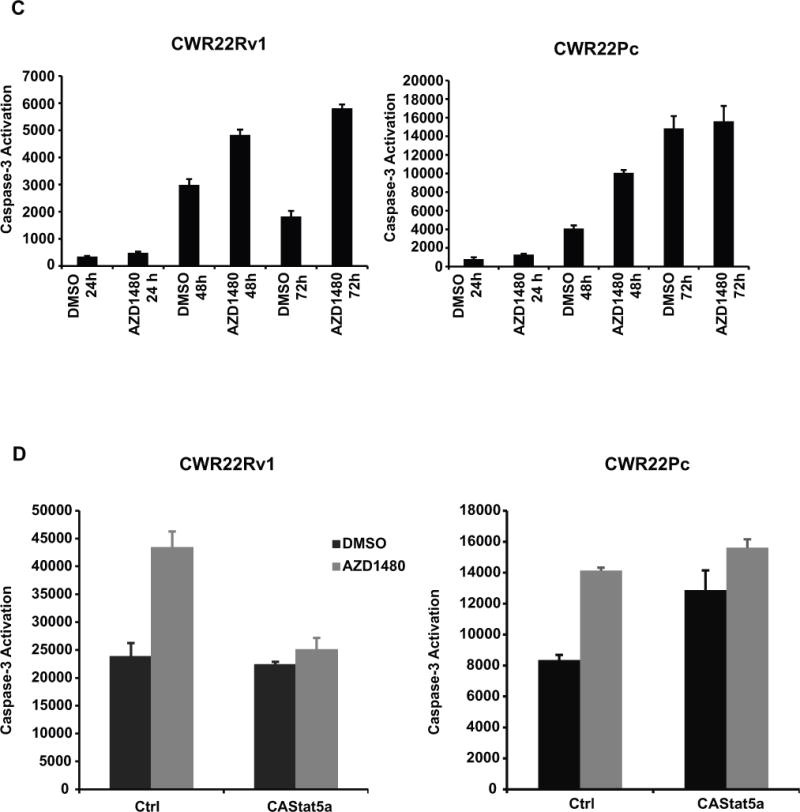
(A) AZD1480 reduces the number of viable CWR22Rv1 and CWR22Pc cells in culture. CWR22Rv1, CWR22Pc, PC3, DU145 and normal prostate epithelial cells (RC165N) were treated with AZD1480 at indicated concentrations for 72 h, and the fraction of viable cells was determined by MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide) metabolic activity assay. (B) AZD1480 increases the fraction of dead PC cells in cell cycle analysis. CWR22Pc cells were treated with AZD1480 for 24, 48 or 72 h at indicated concentrations followed by FACS analysis. (C) AZD1480 increases caspase-3 activation in CWR22Rv1 (72 h) and CWR22Pc cells (48 h). CWR22Rv1 cells were treated with AZD1480 (800 nM) or vehicle followed by determination of caspase-3 activation by fluorometric immunosorbent enzyme assay. (D) AZD1480 induction of caspase-3 activation in CWR22Rv1 and CWR22Pc cells is counteracted by expression of constitutively active (CA) Stat5a/b. CWR22Rv1 and CWR22Pc cells were infected with adenovirus expressing constitutively active Stat5a (AdCAStat5a; MOI 2) 6 h prior to the treatment of cells with AZD1480 (800 nM) for 72 h.
