Figure 4. AZD1480 decreases levels of nuclear Stat5a/b, resulting in loss of CWR22Pc xenograft tumor cell viability. (A) AZD1480 decreases levels of nuclear Stat5a/b in CWR22Pc tumors.
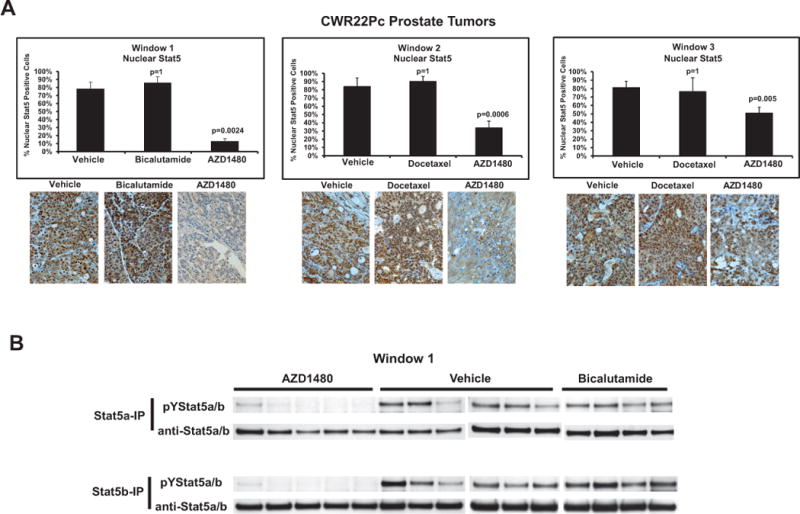
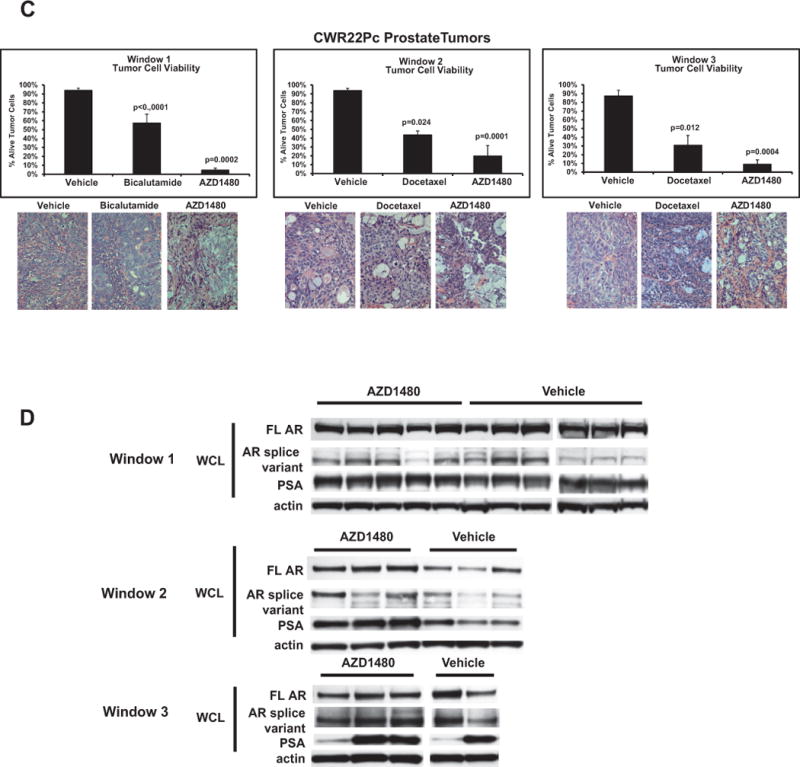
(A) AZD1480 decreased the levels of nuclear Stat5a/b in CWR22Pc xenograft tumors in all treatment windows (TWs). Nuclear Stat5a/b levels were detected by immunohistochemistry in paraffin-embedded tissue sections of the tumors using biotin-streptavidin-amplified peroxidase-antiperoxidase immunodetection. (B) Immunoprecipitation of Stat5a/b from tumor lysates, normalized by protein content and followed by immunoblotting with anti-pYStat5a/b mAb. The filters were stripped and re-blotted with anti-Stat5a/b mAb to demonstrate equal loading. (C) AZD1480 decreases cell viability in CWR22Pc xenograft tumors in all TWs. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of the CWR22Pc tumor sections demonstrated a loss of viable tumor cells and accumulation of dead cells in AZD1480-treated CWR22Rv1 xenograft tumors vs. controls in TWs 1, 2 and 3. (D) Full-length androgen receptor (AR) and AR splice variant protein levels are unaffected by AZD1480 treatment. CWR22Pc tumors in TWs 1, 2 and 3 were evaluated for protein levels of full-length AR, AR splice variants and PSA by immunoblotting of tumor cell lysates normalized for equal protein content with anti-AR mAb, anti-PSA pAb and anti-actin pAb.
