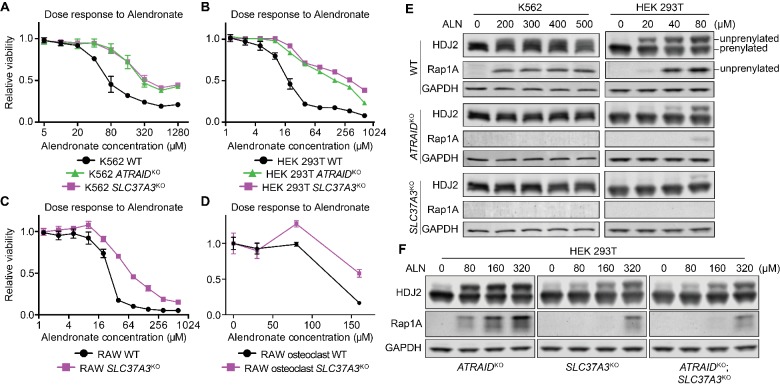
Figure 2. SLC37A3 and ATRAID are functionally related genes required for the mechanism of action of N-BPs.
(A–D) Dose response curves of wild-type, ATRAIDKO and SLC37A3KO K562 cells (A) and HEK 293 T cells (B), and wild-type and SLC37A3KO RAW cells (both undifferentiated macrophages, (C), and differentiated osteoclasts, (D) to alendronate. Cells were treated with a series of doses of alendronate (x-axis) for 48 hr. Relative cell viability was determined by measuring post-treatment total cellular ATP levels and normalizing to those in untreated cells (y-axis). Data depict mean with s.d. for biological triplicate measurements. (E) Immunoblots measuring alendronate-induced reduction in protein prenylation in wild-type and knockout K562 and HEK 293 T cells. Cells were treated with indicated doses of alendronate for 24 hr before analysis by immunoblotting. (F) Immunoblots comparing alendronate-induced reduction in protein prenylation in single and double-knockout HEK 293 T cells. Experimental procedure is as in (C). Note that higher alendronate doses were used in (F) compared to (E) to induce detectable levels of unprenylated proteins. ALN: alendronate.