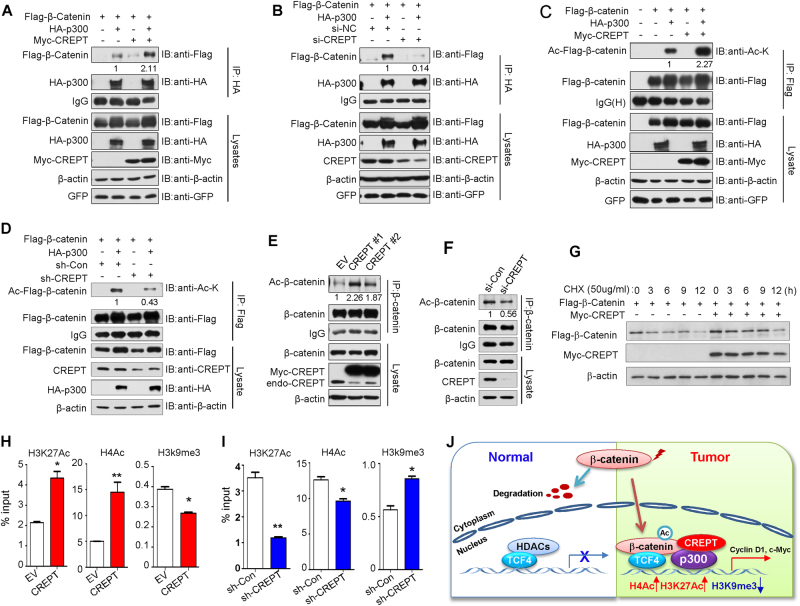
Fig. 7.
p300 promoted acetylation and stability of β-catenin and regulated the epigenetic changes on the promoter of Wnt target genes. a CREPT enhanced the interaction between p300 and β-catenin. b Depletion of CREPT diminished the interaction between p300 and β-catenin. c The acetylation level of ectopic β-catenin was greatly enhanced in DLD-1 cells co-transfected with CREPT and p300. d CREPT knockdown in SW480 cells led to reduced acetylation level of ectopic β-catenin induced by p300. e CREPT overexpression caused increased acetylation level of endogenous β-catenin in DLD-1 cells. f The acetylation level of endogenous β-catenin was reduced in CREPT knockdown SW480 cells. g CREPT reduced the rate of β-catenin degradation after cycloheximide addition. h CREPT upregulated the level of H3K27ac and H4ac and downregulated the level of H3K9me3 on the c-MYC promoter region in DLD-1 cells. The relative fold enrichment of H3K27ac, H4ac, and H3K9me3 at the c-MYC promoter region was determined by ChIP analysis using chromatin prepared from CREPT-overexpressing and control DLD-1 cells. i CREPT depletion led to decreased level of H3K27ac and H4ac and elevated level of H3K9me3 in the c-MYC promoter region in SW480 cells. j Proposed mechanistic model of oncogenic function of CREPT in colorectal cancer