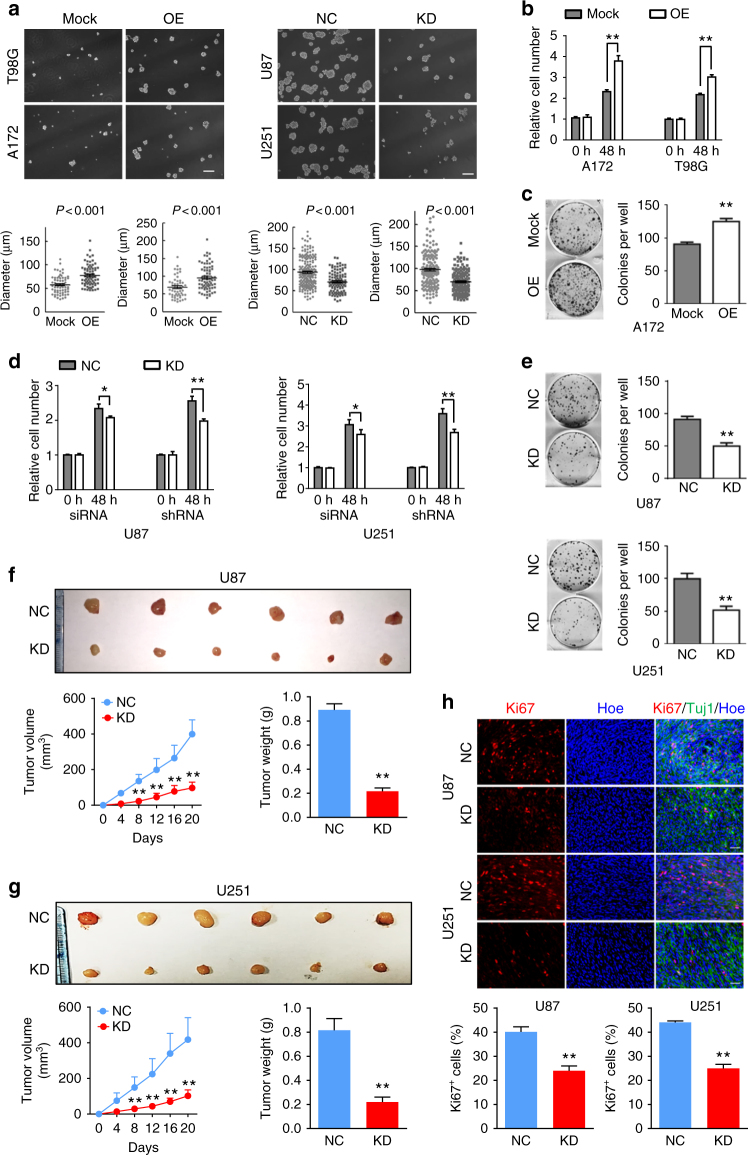
Fig. 2.
Smad6 promotes tumor sphere formation, cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of GBM cells. a Nuclear-Smad6 promoted tumor sphere formation of GBM cells. Representative images of in vitro tumor sphere formation in T98G and A172 cells with adenovirus mediated nuclear-Smad6 OE (upper panel) and U87 and U251 cells with lentivirus-mediated Smad6 knockdown (KD; lower panel). Scale bars, 200 μm. b Nuclear-Smad6 OE promoted cell growth in both A172 and T98G cells (n = 6). c Nuclear-Smad6 OE increased colony formation of A172 cells (n = 3). d Depletion of Smad6 by siRNA or Lenti-shRNA inhibited cell growth in both U87 and U251 cells. (n = 6). e Depletion of Smad6 impaired colony formation of U87 and U251 cells (n = 3). f, g Smad6 depletion inhibited tumor growth in nude mice. Mean tumor volumes and average tumor weight of xenografts of U87 (f) and U251 (g) with Smad6 KD were significantly decreased compared with their corresponding controls (n = 6). h Smad6 KD impaired proliferation of tumor cell derived from U87 and U251 cells. The representative double IF images of xenograft tumor sections with Ki67 and Tuj-1 (upper panel) and the quantification of (lower panel) the fraction of Ki67-positive cells. Positive cells were quantified n = 20 randomly selected fields per mouse (n = 6). Scale bars, 50 μm. Data were represented as means ± SD and analyzed using unpaired Student’s t-test in a, two-tailed Student’s t-test in b–h. **P < 0.01