Fig. 8.
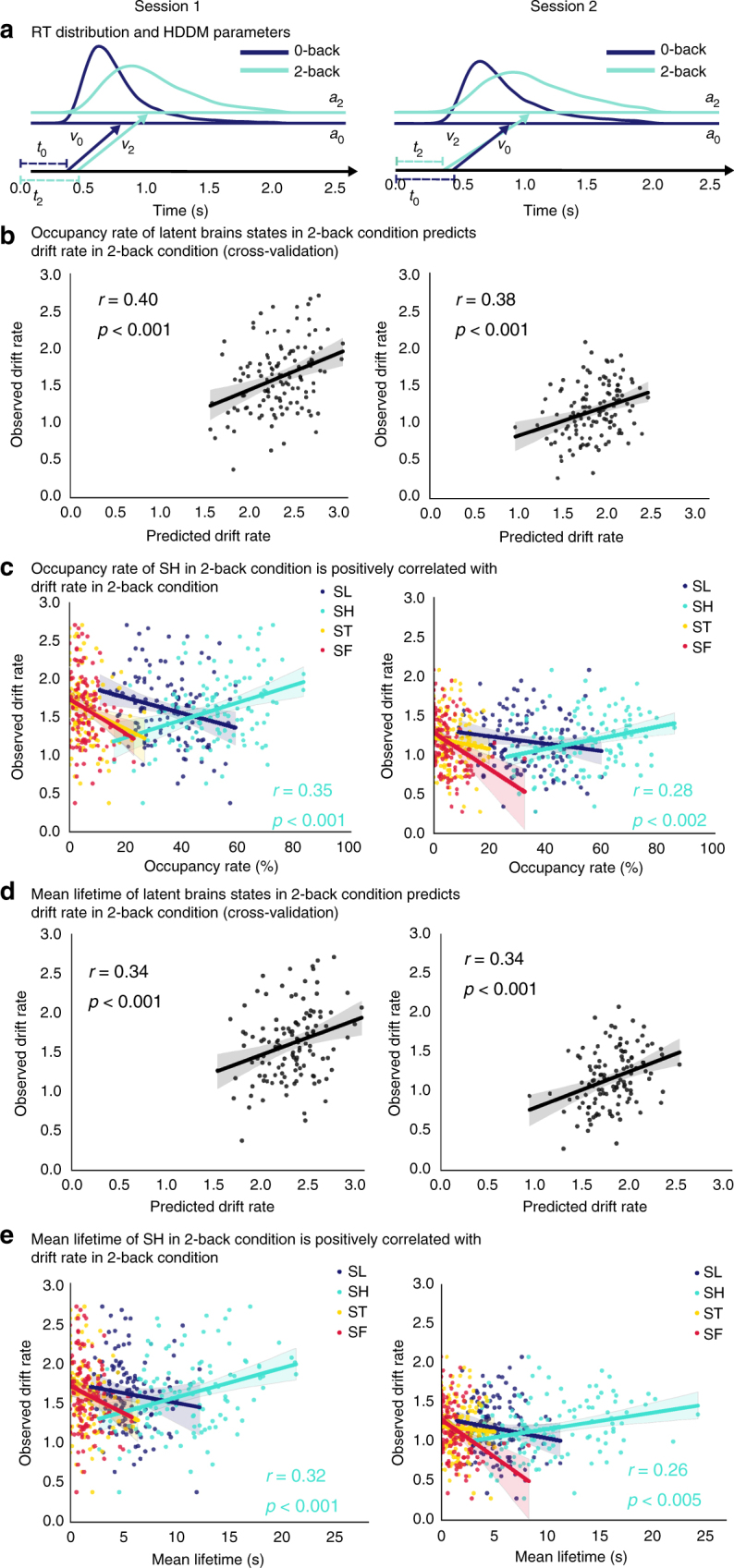
Occupancy and mean lifetimes of latent brain state predict decision-making dynamics. a Illustration of hierarchical drift-diffusion model (HDDM) and parameter estimates based on the distribution of reaction times (RTs) in the 2-back and 0-back task conditions. b A multiple linear regression model was trained using occupancy rates of latent brain states in the 2-back task to predict drift rate in the WM task. A significant association was found, and predicted accuracy was correlated with observed accuracy in both sessions (Session 1: r = 0.40, p < 0.001; Session 2: r = 0.38, p < 0.001, Pearson’s correlation). c Occupancy rate of the latent brain state SH which dominates the 2-back WM task condition was correlated with WM task drift rate in both sessions (Session 1: r = 0.35, p < 0.001; Session 2: r = 0.28, p < 0.002, Pearson’s correlation). No such relations were found for any of the other latent states. d A multiple linear regression model was trained using mean lifetimes of latent brain states in the 2-back task to predict drift rate in the WM task. A significant accuracy was found with predicted accuracy was correlated with observed accuracy in both sessions (Session 1: r = 0.34, p < 0.001; Session 2: r = 0.34, p < 0.001, Pearson’s correlation). No such relations were found for any of the other latent states. e Mean lifetimes of the latent brain state SH which dominates the 2-back WM task was positively correlated with WM task drift rate in both sessions (Session 1: r = 0.32, p < 0.001; Session 2: r = 0.26, p < 0.005, Pearson’s correlation). No such relations were found for any of the other latent states. Shaded area represents 95% confidence interval. Color code mapping in c and e: dark blue—SL, cyan—SH, yellow—ST, red—SF
