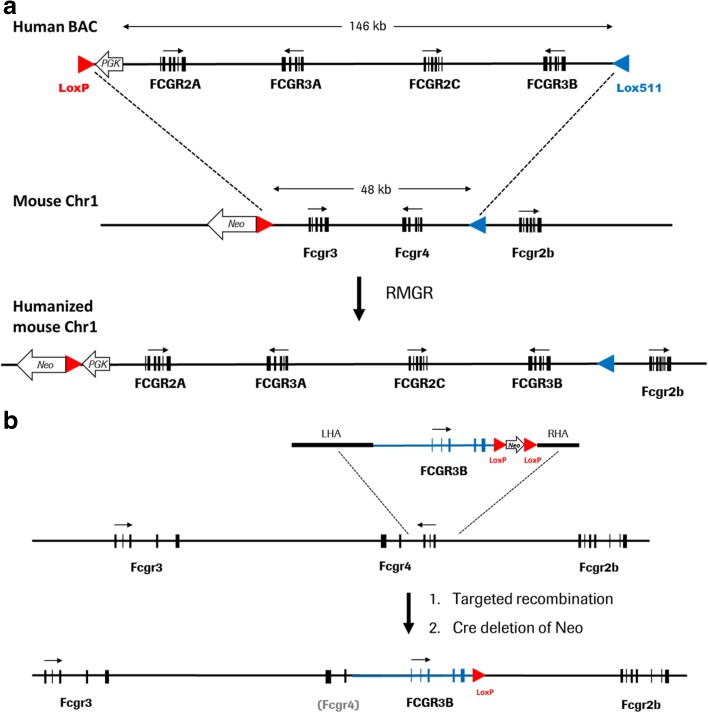
Fig. 1.
Construction of humanized mouse strains HFCGR2–3 and HFCGR3B. Representations not drawn to scale. (a), HFCGR2–3: Recombination-mediated genomic replacement (RMGR) of mouse genes Fcgr3 and Fcgr4 with human genes FCGR2A, FCGR2C, FCGR3A and FCGR3B. Upper line: BAC vector used encompassing human 146 kb sequence from 1:161494582 to 1:161640325 of human Chr1_q23.3, in GRCh38. Middle line: replaced 48 kb genomic region between positions 1:171015025 to 1:171062982 of mouse Chr1 in mm10 GRCh38. Lower line: humanized mouse locus with inserted human FcgR genes. (b), HFCGR3B: Targeted gene replacement of mouse Fcgr4 gene with the human FCGR3B gene. Upper line: targeting vector composed of 13 kb sequence from 1:161623196 to 1:161636203 of human Chr1_q23.3, in GRCh38 bearing the human FCGR3B gene and flanking mouse sequences adjacent to the first and third Exon of mouse Fcgr4 gene. Middle line: Scheme of the mouse Fcgr locus. Lower line: targeted mouse locus with human FCGR3B gene replacing the inactivated mouse Fcgr4 gene (grey in parenthesis). Human genes are indicated in big capitals, mouse genes in small capitals. LHA and RHA indicate left homology and right homology arm, respectively. Red and blue arrowheads represent LoxP and Lox511 elements, respectively. White block arrows indicate Neo gene or PGK promoter. Small arrows indicate direction of transcription. The allelic variants of the human FcγR genes used here are FCGR2B (131R), FCGR2C (Stop variant), FCGR3A (128F) and FCGR3B (NA1).