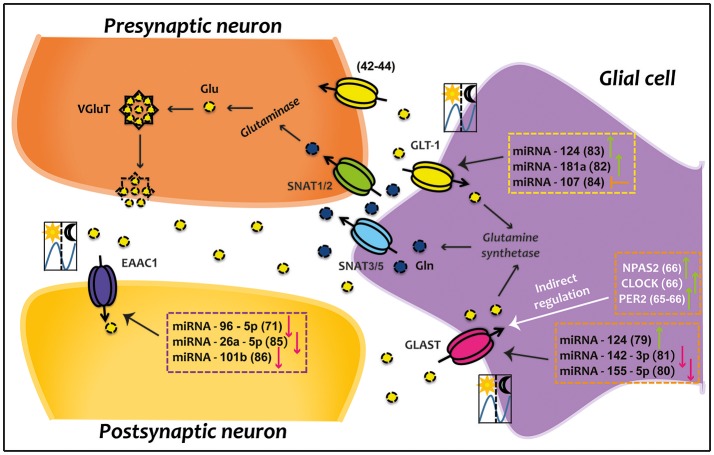
Figure 1.
Direct and indirect circadian regulation of EAATs. Glutamatergic synapse which is composed of presynaptic neuron, postsynaptic neuron and glial cell compartment are represented. Some clock genes indirectly up-regulate GLAST; while several miRNAs directly down- or up-regulate GLAST, GLT-1, and EAAC1. Green arrows represent up-regulation, red arrows indicate down-regulation, and orange arrow denotes inhibition. The illustration of day/night indicates that transporter present a circadian rhythm in 12/12 h light/dark conditions. Numbers in parentheses refer to cited publications. CLOCK, circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; EAAC1, excitatory amino acid carrier 1; GLAST, glutamate aspartate transporter; Gln, glutamine; GLT-1, glutamate transporter 1; Glu, glutamate; NPAS2, neuronal PAS domain-containing protein 2; PER2, period 2; SNATs, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporters; VGluT, vesicular glutamate transporter.