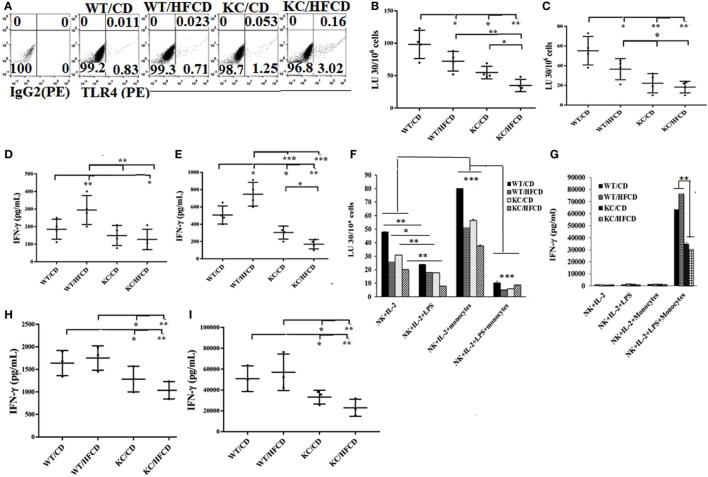
Figure 1.
Natural killer (NK) cells from KC mice fed with control diet (CD) or high-fat calorie diet when cultured with autologous monocytes demonstrated less cytotoxicity and decreased IFN-γ secretion when compared to WT mice fed with CD. WT and KC mice were fed with a CD or high-fat calorie diet as described in Section “Materials and Methods.” Splenocytes were harvested after animals were sacrificed and single cell suspension was prepared as described in Section “Materials and Methods” and used to purify NK cells. TLR4 surface expression on the purified NK cells from four groups of mice was analyzed using antibody staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. One of three representative experiments is shown in the (A). Purified NK cells from splenocytes were activated with IL-2 (10,000 U/ml) (n = 4) (B,D) or with IL-2 (10,000 U/ml) in the presence of LPS (100 ng/ml) (n = 4) (C,E) before they were used as effector cells in a standard 4-h 51Chromium release assay. The lytic units (LUs) 30/106 cells were determined using the inverse number of NK cells required to lyse 30% of the ST63 cells ×100 (n = 4) (B,C), and the supernatants were harvested after culture to determine the levels of IFN-γ secretion (n = 4) (D,E). IL-2-treated and IL-2 and LPS-treated NK cells as described in (C,E) were cultured with or without autologous monocytes at NK:monocytes; 1:0.5 ratio before they were used as effector cells in a standard 4-h 51Chromium release assay. The lytic units (LUs) 30/106 cells were determined using the inverse number of NK cells required to lyse 30% of the ST63 cells ×100. One of five representative experiments is shown in (F). The supernatants were harvested to determine the levels of IFN-γ secretion. One of five representative experiments is shown in the (G). IL-2-treated NK cells (H) and IL-2 and LPS-treated NK cells (I) were cultured with autologous monocytes at NK:monocytes; 1:0.5 ratio before the supernatants were harvested to determine the levels of IFN-γ secretion (n = 3).