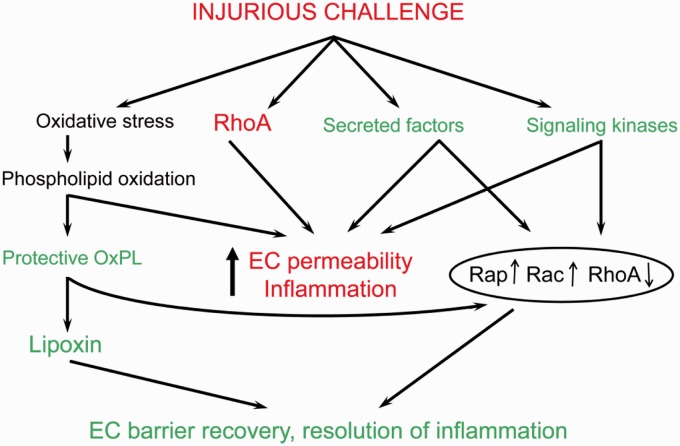
Fig. 3.
Balance of EC-disruptive and EC-protective mechanisms in the course of lung injury and resolution phase. Lung injurious factors (bacterial pathogens, excessive mechanical stretch, cytokines, disruptive bioactive molecules) trigger pathologic signaling (i.e. oxidative stress, RhoA pathway, signaling kinases, secreted factors) leading to endothelial hyperpermeability, inflammation, and lung dysfunction. However, pathologic stimuli also activate mechanisms of auto-recovery such as secretion of pro-survival growth factors and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators which suppress inflammation, downregulate pro-inflammatory and disruptive RhoA GTPase-mediated pathways, and stimulate Rap1 and Rac1 GTPase-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling leading to EC barrier recovery.