Figure 5.
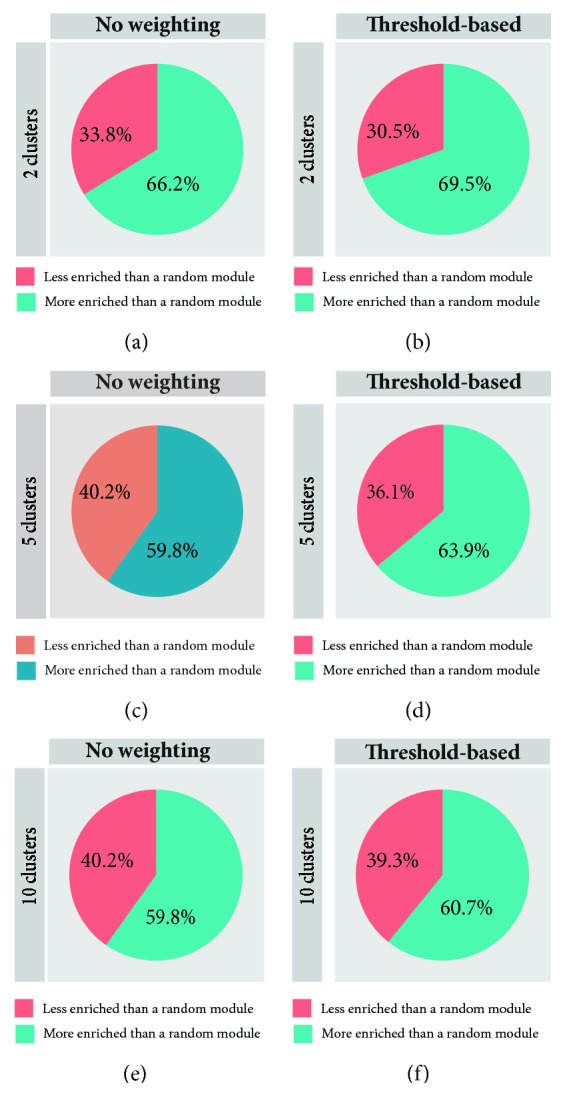
Comparing epitranscriptome module detection based on biological significance. The epitranscriptome modules identified from clustering analysis are always more likely to be biologically meaningful than the random modules, and this is true for clustering analysis using the measurement weighting strategy (66.2%, 59.8%, and 59.8% when k = 2, 5, and 10, respectively). The results obtained with measurement weighting scheme consistently outperform those obtained without measurement weighting (69.5% vs 66.2 when k = 2, 63.9% vs 59.8% when k = 5, and 60.7% vs 59.8% when k = 10), suggesting the proposed threshold-based measurement weighting strategy is helpful to improve clustering result and find more biological meaningful epitranscriptome modules. Clustering analysis with or without measurement weighting strategy was applied to 3000 random selected RNA methylation sites, and the epitranscriptome modules identified are compared with random group of genes of the same size in terms of biological significance using gene ontology enrichment analysis. Using bootstrap sampling approach, the analysis was repeated for 100 times and the results are summarized in this figure.
