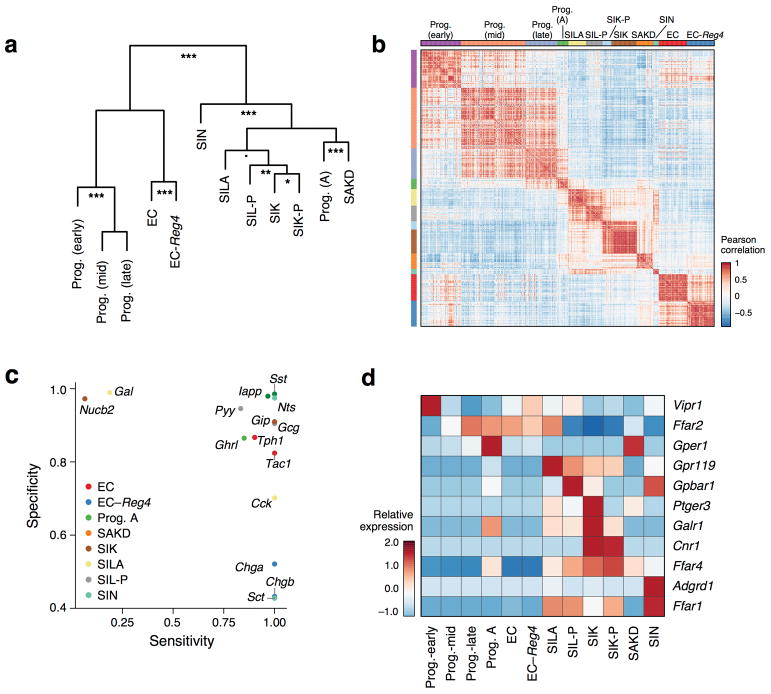
Extended Data Figure 6. Classification and specificity of enteroendocrine subsets related to Figure 3.
a–b. Relationships between EEC subsets. (a) Dendrogram shows the relationship between EEC clusters as defined by hierarchical clustering of mean expression profiles of all the cells in a subset (Methods). Estimates for the significance of each split are derived from 100,000 bootstrap iterations using the R package pvclust (■ p<0.1, * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01, p < 0.001, χ2 test). (b) Heatmap shows cell-cell similarities (Pearson’s r, color bar) between the 11 significant PCs scores (p<0.05, Methods) across the 533 EECs (rows, columns). Rows and columns are ordered using cluster labels obtained using unsupervised clustering (Methods). c. Subset specificity of gut hormones and related genes. Scatter plot shows each gene’s specificity to its marked cell subset (y axis; defined as the proportion of cells not in a given subset which do not express a given gene) and its sensitivity in that subset (defined as the fraction of cells of a given type which do express the gene, Methods). Subsets are color coded as in the legend. Genes are assigned to the subset where they are most highly expressed on average. Genes were chosen based on their known annotation as gut hormones (Cck, Gal, Gcg, Ghrl, GIP, Iapp, Nucb2, Nts, Pyy, Sct, Sst), enterochromaffin markers (Tph1, Tac1) and canonical EEC markers (Chga, Chgb). d. GPCRs enriched in different EEC subtypes. Heatmap shows the expression levels (row-wise Z-score, color bar) averaged across the cells in each of the EEC sub-types (columns) of 11 GPCR-encoding genes (rows) that are differentially expressed (FDR <0.25, Mann-Whitney U-test) in one of the EEC subtype clusters. The free fatty acid receptors (Ffar) 1 and 4 show specific expression patterns: Ffar1 highest in SIN cells, and also expressed by the Cck-expressing subsets previously termed I-cells (SIL-P, SILA and SIK-P), while Ffar4 is highest in the GIP-expressing subsets (SIK and SIK-P). These receptors are known to induce the expression of GIP and Gcg to maintain energy homeostasis1. Ffar2 was expressed by some progenitors and by EC cells, but notably absent from GIP-expressing cells, while the oleoylethanolamide receptor Gpr119, important for food intake and glucose homeostasis2, is expressed highest in SILA cells.