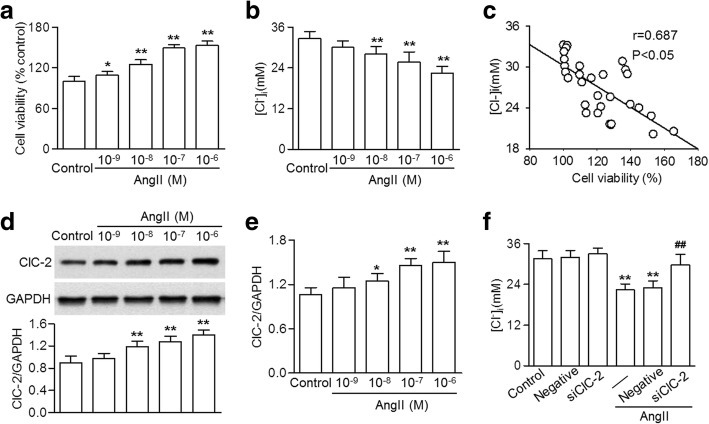
Fig. 1.
ClC-2 knockdown inhibited the AngII-induced efflux of Cl− in HBVSMCs. a HBVSMCs were treated with angiotensin II (AngII) at different concentrations (10− 9, 10− 8 10− 7 and 10− 6 M) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 assay. b Intracellular Cl− concentration [Cl−]i was examined using an MEQ fluorescence probe. c The correlation between [Cl−]i and cell viability was analyzed. d and e – The expression of ClC-2 in the cells treated as described in (a) was examined using western blotting (d) and quantitative real-time PCR (e). f Cells were treated with ClC-2 siRNA (20 nM) or negative siRNA for 48 h before AngII incubation (10− 7 M) for a further 48 h. [Cl−]i was examined. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. control, ##p < 0.01 vs. AngII alone, n = 6