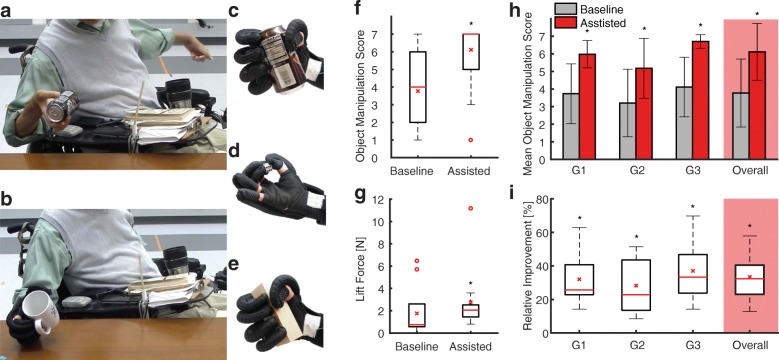
Fig. 3.
Soft robotic glove for hand function restoration: a Study participant during unassisted object manipulation using a passive tenodesis grasp to lift an object (baseline condition) b Study participant performing an active palmar grasp to manipulate an object using the soft robotic glove (assisted condition). c Soft robotic glove assisting palmar grasp d Soft robotic glove assisting pinch grasp e. Soft robotic glove assisting the grasp of a wooden block to assess lift force f Improvement in TRI-HFT score across all participants (N = 9; baseline mean = 3.77, median = 4; assisted mean = 6.11, median = 7; mean difference = 2.34; 95% confidence interval from 1.67 to 3.01; p < 3e-11) g Improvement in mean lift force across all participants (N = 9; baseline mean = 1.76 N, median = 0.68 N; assisted mean = 2.76 N, median = 2.03 N; mean difference = 1.00 N; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Z = − 4.28, p < 2e-5) h Mean object manipulation scores of palmar grasp (G1), pinch grasp (G2) and wooden block strength (G3) subtests. The mean score difference between the baseline and assisted condition is significant and consistent throughout all subgroups (see 2F). The average scores between the groups differ significantly (Linear Mixed Model Coefficient Test, G1/G2; F = 18.81, p < 2e-4, G2/G3; F = 10.63, p < 1.5e-3, G2/G3; F = 6.85 p < 0.01) i Subgroup specific improvement of the TRI-HFT score from baseline to the assisted condition, relative to the maximum value = 7 (G1 mean = 32.06%, median = 25.71%; G2 mean = 28.25%, median = 22.85%; G3 mean = 37.04%, median = 33.33%; overall mean = 33.42%, median = 31.85%). * indicates significant difference with respect to the baseline condition, red stars denote means, red lines denote medians, red circles denote outliers defined as data points outside the range of 1.5 times the interquartile range