Fig. 3.
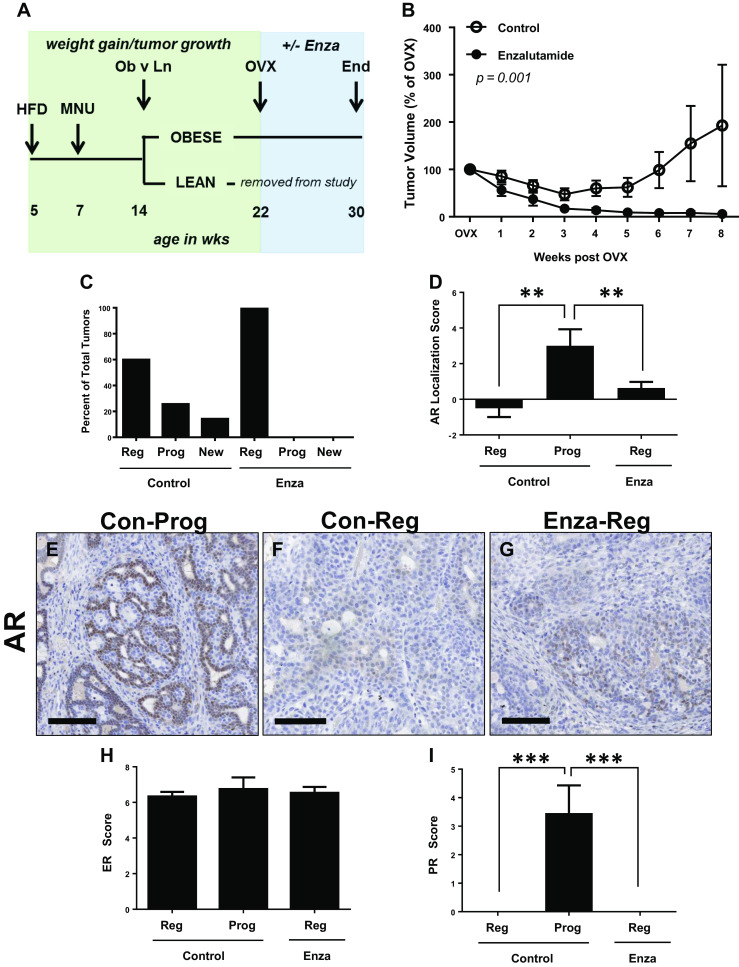
Enzalutamide treatment inhibits tumor progression in obese rats after OVX. a Schematic study design. HFD high fat diet, MNU N-methyl-N-nitrosourea, OVX ovariectomy. Lean rats were used for another study. Enzalutamide was administered for 8 weeks beginning at OVX, indicated by the blue box. b Tumor volume from control (empty circle) and enzalutamide-treated (filled circle) rats, represented as percent of that at OVX; p = 0.001 by ANOVA. c Percent of total tumors from the end of study that were regressing (reg) or progressing (prog) from the time of OVX, or that were newly formed (new) after OVX in Control (N = 19) and enzalutamide-treated (N = 11) rats; p = 0.007 by chi-square analysis. d AR localization scores in regressing and progressing tumors (N = 4–11 tumors per group). Representative images of AR immunostaining in e progressing and f regressing tumors from control rats, and in a g regressing tumor from enzalutamide-treated rat (g). Scale bars = 100 μm. h ER scores, and i PR scores in regressing (reg) and progressing (prog) tumors from control and enzalutamide-treated rats (N = 11–12 tumors per group). Mann-Whitney tests determined statistical significance for steroid hormone receptor levels. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
