Figure 8.
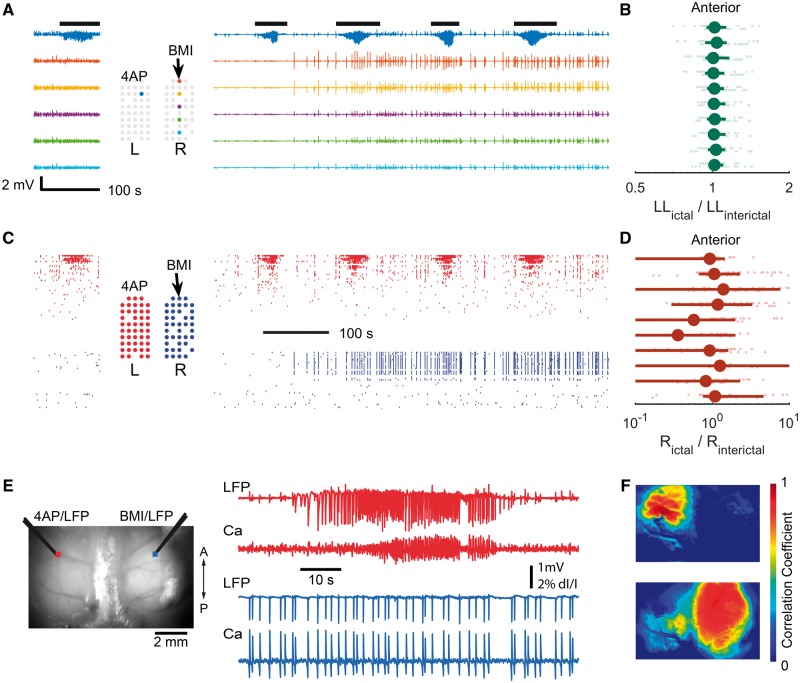
Contralateral BMI injection failed to induce cross-hemisphere propagation. (A) 4-AP is injected to create a seizure focus in the left hemisphere. LFP before (left) and after (right) BMI injection in the contralateral homotopic somatosensory cortex. After BMI injection, paroxysmal interictal spikes were seen in the LFP; however, a second ictal focus did not develop. (B) Ictal line length relative to the interictal period following each ictal event. Data were plotted similarly to Fig. 1E. , 17 ictal events from two animals, 675 data points, sign test P = 0.805. (C) Multiunit raster plot before (left) and after (right) BMI injection. Time is aligned with A. (D) Average ictal multiunit firing rate (R) relative to interictal, analogous to B. , sign test, P = 0.98. (E) Wide field calcium imaging of 4-AP ictal focus in the left hemisphere and focal disinhibition with BMI injected at the contralateral homotopic cortex. Left: The field of view showing the injection sites. Right: The LFP and calcium fluorescence signal recorded from 4-AP (top) and BMI (bottom) injection sites. The ictal events do not propagate to the contralateral side and the BMI injection results in focal interictal spikes without creating a new interconnected ictal focus. (F) Seed-initiated correlation coefficient maps. Top: The seed trace used was taken from a region of interest adjacent to the 4-AP injection site. Bottom: The seed trace used was taken from a region of interest adjacent to the BMI injection site. The ictal event remains focal and does not involve the other hemisphere. The disinhibited interictal spiking zone is widespread and completely independent from the seizure focus.