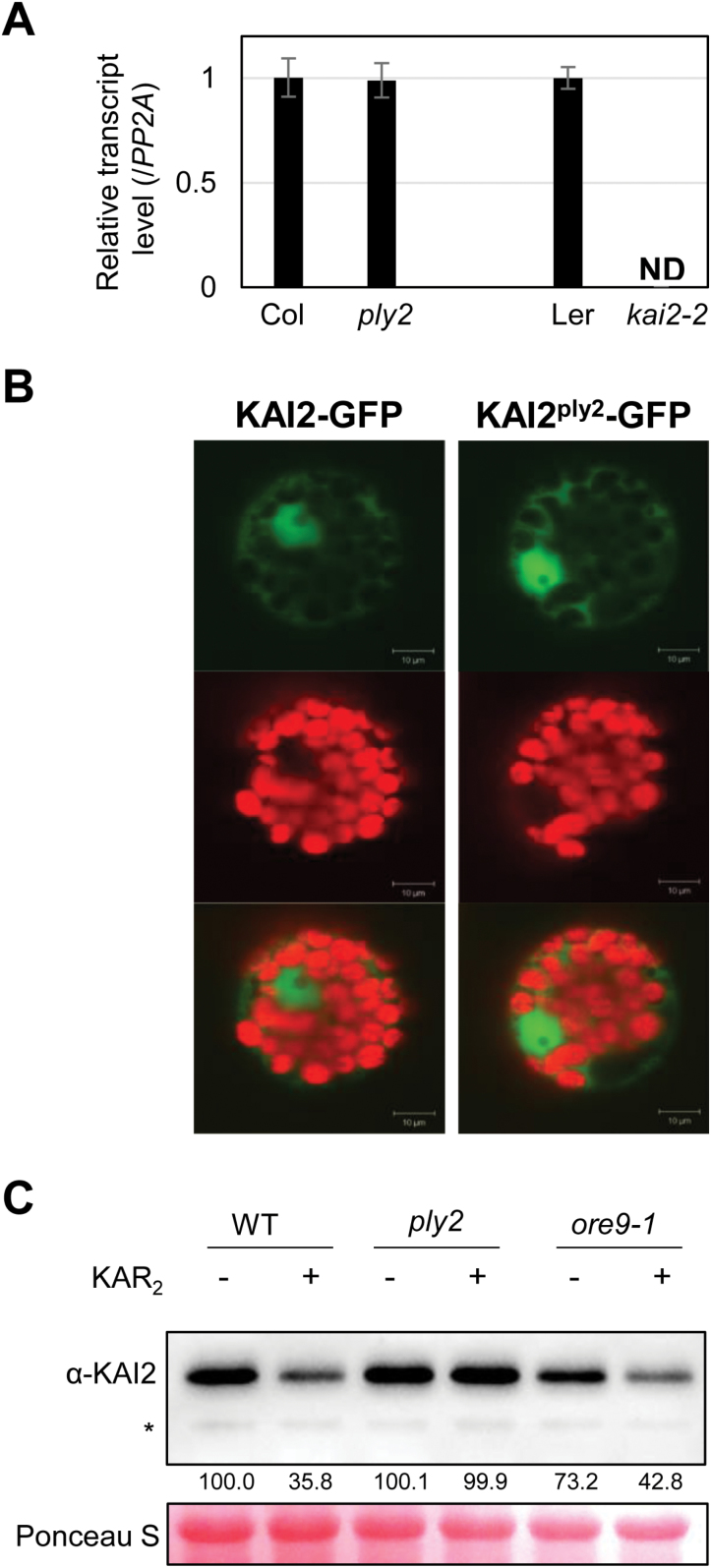
Fig. 4.
Functional assay of the KAI2ply2 mutation. (A) Expression analysis of the KAI2 transcript. Total RNA from 5-d-old light-grown seedlings was used for qRT-PCR analysis. PP2A was used as a loading control. The relative expression of the KAI2 transcript in the ply2 or kai2-2 mutant was compared to that in the wild-type, which was set to 1. Data are means (±SD) of experimental replicates (n=3). ND, not detected. (B) Subcellular localization of KAI2. The wild-type KAI2-GFP or KAI2ply2-GFP constructs were transfected to Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. Representative images taken by confocal microscopy are shown: GFP signal (upper), chloroplast auto-fluorescence (middle), merged image (lower). (C) Immunoblot analysis of the KAI2 protein. Total proteins were extracted from seedlings grown under continuous light for 7 d after treatment with a mock solution (–) or 10 μM KAR2 (+) for 2 h. The KAI2 protein (29.8 kDa) was detected using an α-KAI2 antibody. The transferred proteins were stained with Ponceau S solution as a loading control. Numbers below the bands indicate the relative densitometry values of the KAI2 protein band, normalized to those of the loading control. The asterisk indicates a non-specific protein.