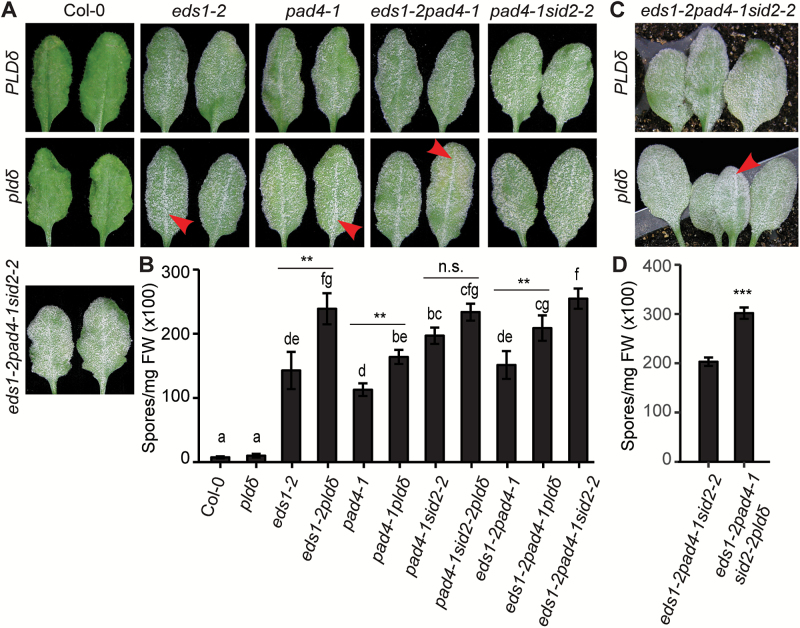
Fig. 5.
PLDδ in Arabidopsis contributes to post-penetration resistance via an SA- and EDS1/PAD4-independent pathway.(A, C) Representative leaves of the indicated genotypes (defined by name IDs from both x- and y-axes) infected with Gc UMSG3 at 11 dpi. Note that fungal mass is more noticeable on leaves, especially the mid-vein area (arrowheads), from eds1-2pldδ, pad4-1pldδ, eds1-2pad4-1pldδ, and eds1-2pad4-1sid2-2pldδ than the corresponding leaves from eds1-2, pad4-1, eds1-2pad4-1, and eds1-2pad4-1sid2-2 (upper panel). (B, D) Quantification of spore production in the indicated genotypes in (A, C), respectively, at 11 dpi normalized to leaf FW. Data represent the mean ±SEM of four samples (n=4, 4–5 leaves each) from one experiment, which was repeated three times with similar results. Different lower case letters indicate statistically different groups as determined by multiple comparisons using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s HSD test (B, **P<0.01), or by Student’s t-test (D, ***P<0.001). n.s., not significant.