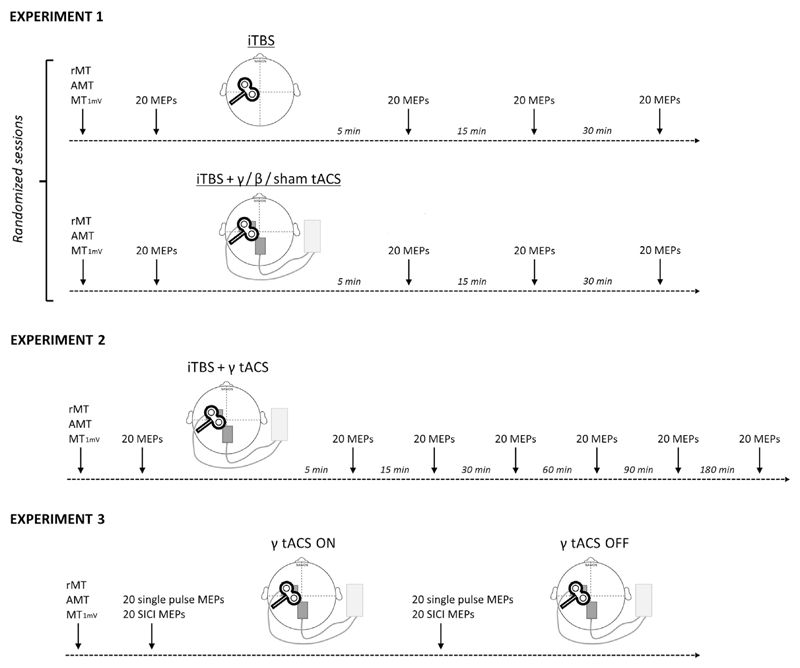
Fig. 1. Experimental design.
The early part of every experiment consisted in identifying the hotspot of the first dorsal interosseous muscle and estimating the resting motor threshold (RMT), active motor threshold (AMT) and intensity that induced a motor evoked potential of about 1 mV in amplitude (MT1mV). Experiment 1: effect of iTBS-tACS co-stimulation. Twenty single TMS pulses were delivered, at rest, before and 5, 15 and 30 min after the intermittent theta burst (iTBS) protocol. The four different sessions were conducted in a random order at least one week apart. Experiment 2: time course of iTBS-γ tACS co-stimulation. Twenty single pulse MEPs were recorded before and 5, 15, 30, 60, 90 and 180 min after the iTBS-γ tACS protocol. Experiment 3: effect of γ tACS on corticospinal excitability and GABA-A interneurons. Twenty single TMS pulses and twenty paired (SICI protocol) TMS pulses were delivered in a random order, at rest, before tACS was activated and during γ tACS stimulation on M1.