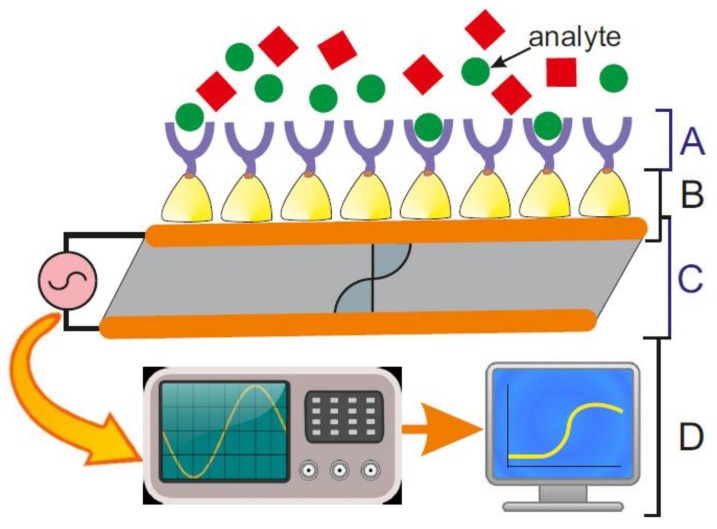
Figure 1.
Elements and selected components of an S-layer protein-based quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) biosensor. (A) A biosensing element or bioreceptor comprising of accessible functions like, e.g., an antibody to which the analyte binds with highly specific affinity. (B) An interface architecture comprising of a QCM-D sensor surface covered by a recrystallized S-layer lattice, which provides an environment for the proper functioning of the biosensing element. Here, the specific biological event takes place, which gives rise to a certain physical phenomenon. (C) A transducer converting the physical phenomenon (piezoelectricity) resulting from the analyte’s interaction with the biological element into an electrical signals. (D) Associated electronics comprising of signal amplifier, signal processor and a display allowing for a user-friendly visualization and evaluation of the data.