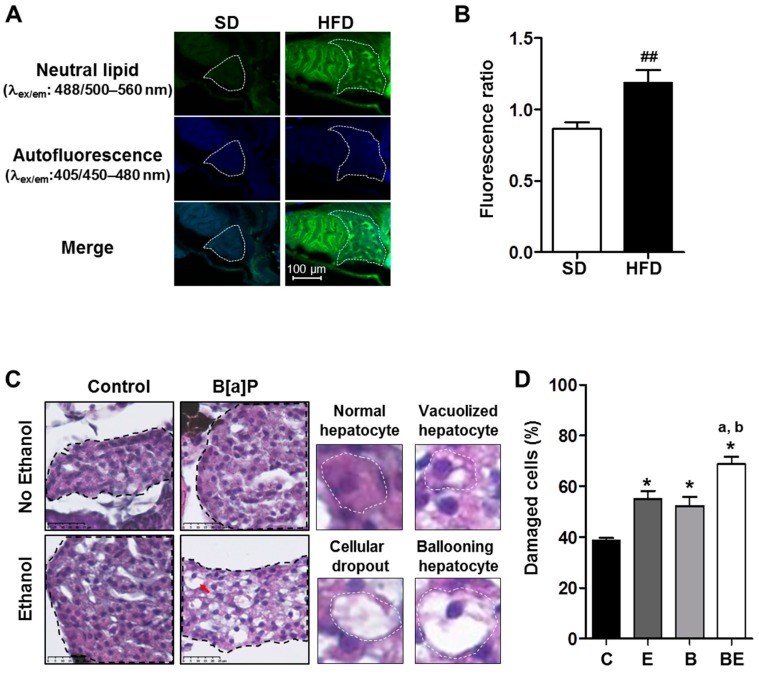
Figure 1.
Progression of high-fat diet (HFD) induced steatosis in zebrafish larvae to a steatohepatitis-like state upon co-exposure to ethanol and benzo[a]pyrene. Zebrafish larvae were fed with a HFD from 4 days post-fertilization (dpf) until 5 dpf and compared to larvae fed with a standard diet (SD) in order to observe the development of steatosis at 5 dpf (A,B). Lipid accumulation was analyzed after Nile red staining in HFD larvae as well as in SD larvae using confocal microscopy (excitation/emission (ex/em) wavelength: 488/500–560 nm, magnification ×400). (A) Representative images of larva staining are presented in which the liver has been outlined in white. (B) In order to estimate the relative amount of neutral lipids in the liver, the ratio of fluorescence intensity was calculated from images of more than 15 larvae per diet as follows: Fluorescence ratio = (intensity of neutral lipid staining with Nile red (ex/em wavelength: 488/500–560 nm)/(intensity of unspecific staining (autofluorescence; ex/em wavelength: 405/450–480 nm))). Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of at least 12 larvae per diet. Zebrafish larvae fed with HFD from 4 dpf and exposed to ethanol and/or B[a]P for seven days from 5 to 12-dpf to achieve four conditions—untreated (C) or treated with 25 nM B[a]P (B), 43 mM ethanol (E) or a combination of both toxicants (BE,C,D). (C) Liver damage was evaluated on zebrafish liver sections after HES staining (magnification ×400). Black dotted line outlines liver. Histological liver sections were magnified to show, surrounded by the white dotted line, a normal hepatocyte, a vacuolized hepatocyte, a cellular dropout and a ballooning hepatocyte (red arrow). Images are representative of at least five larvae. (D) From images obtained in (C), the histological count of damaged cells was realized. Values are the mean ± SEM of at least five larvae. ## Significantly different from SD larvae; * Significantly different from HFD control larvae; a Significantly different from larvae treated by ethanol only; b Significantly different from larvae treated by B[a]P only.