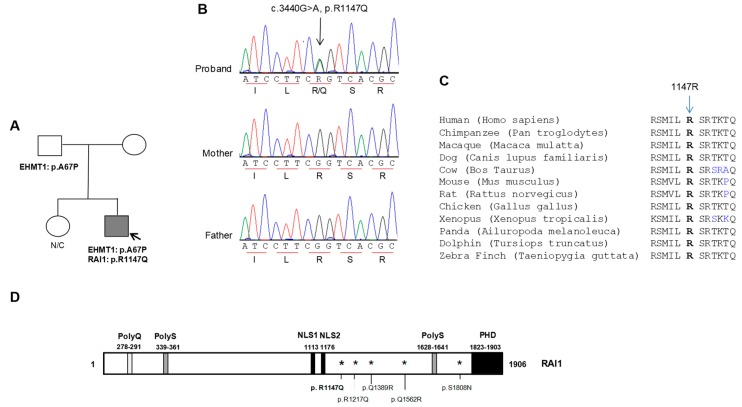
Figure 1.
Molecular analyses of a patient with autism. (A) A partial pedigree of a family with one child with autism. Nonsynonymous variants identified in the proband and his parents are shown. Grey filled symbol, affected autism; (B) Automated sequence chromatograms showing the RAI1 gene variation (arrow) in the proband. Triplet codon (underlined) and translated amino acids are shown; (C) An alignment of a region of human RAI1 showing the highly conserved 1147R residues (in bold type) altered in the proband; (D) Schematic representation of the domains (PolyQ, PolyS, nuclear localization signals (NLS1 and NLS2) and the PHD domain) contained in the RAI1 protein. The p.R1147Q alteration identified in this study is shown in bold. In addition, the previously described and functionally tested p.R1217Q, p.Q1389R, p.Q1562R and p.S1808N mutations are depicted.