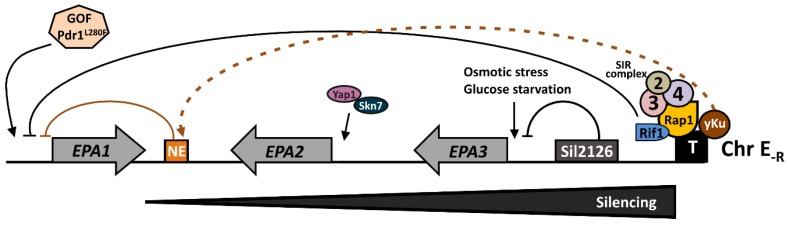
Figure 1.
Map of the right subtelomeric region of chromosome E (E-R) where the EPA1, EPA2, and EPA3 cluster is localized. EPA1 expression is negatively regulated by the cis-acting element called Negative Element (NE, orange rectangle) shown as an orange T arrow, which depends on yKu70 and yKu80 proteins (yKu, brown circle). The dashed orange arrow indicates the genetic requirement of yKu for the activity of NE. EPA2 is induced under oxidative stress and requires Yap1 (purple) and Skn7 (dark blue) transcription factors. EPA3 is repressed by the protosilencer Sil2126 (dark gray rectangle), indicated by the black T arrow from Sil2126 to EPA3 promoter. EPA1, EPA2, and EPA3 are subject to another layer of global regulation called subtelomeric silencing (indicated by a horizontal black triangle below the chromosome and a black T arrow from the telomere to EPA1p). Silencing propagates from the telomere (T) and depends on the SIR complex (Sir2, Sir3, and Sir4) (2, 3, and 4), Rap1 (yellow circle), Rif1 (blue), and yKu proteins. EPA3 expression responds also to osmotic stress and glucose starvation.