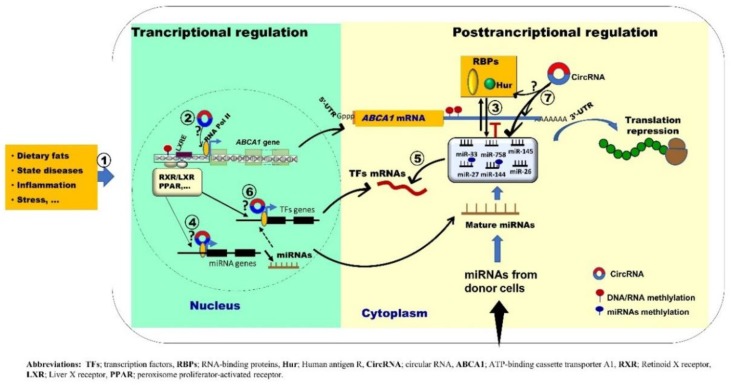
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of proposed scenarios for the mechanisms by which ABCA1 gene expression is regulated. Various factors including nutrition, state diseases, stress and inflammation can alter epigenetic ABCA1 gene regulation in different cells mainly macrophages and hepatocytes (1). At the transcriptional level, ABCA1 gene expression is regulated by key nuclear receptors including LXR family and their heterodimeric partners, retinoic acid receptors (RXR) via functional LXREs (2). At the post-transcriptional level, miRNAs and RBPs (Hur) cooperate/compete for target binding regulation (3). miRNAs and TFs may cooperate to tune gene expression by forming feedback or feedforward loops (4) and (5). CircRNAs may also be part of the interplay by their potential interaction with TFs, miRNAs and RBPs (2), (4), (6) and (7). Finally, the proposed interplay between TFs-miRNAs-RBPs-CircRNAs could be taken into consideration while elucidating epigenetic mechanisms regulating the first step of RCT gene network.