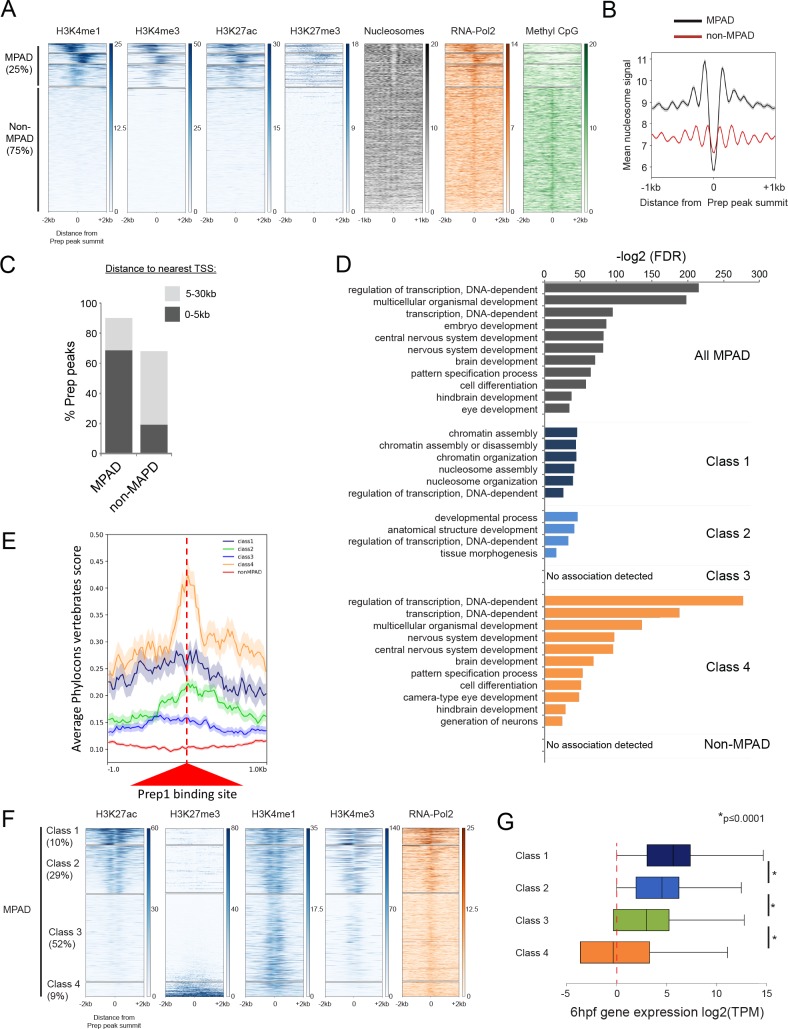
Figure 4. Some TALE-occupied sites are associated with chromatin marks at blastula stages and developmental control genes are enriched near MPADs displaying repressive histone modifications.
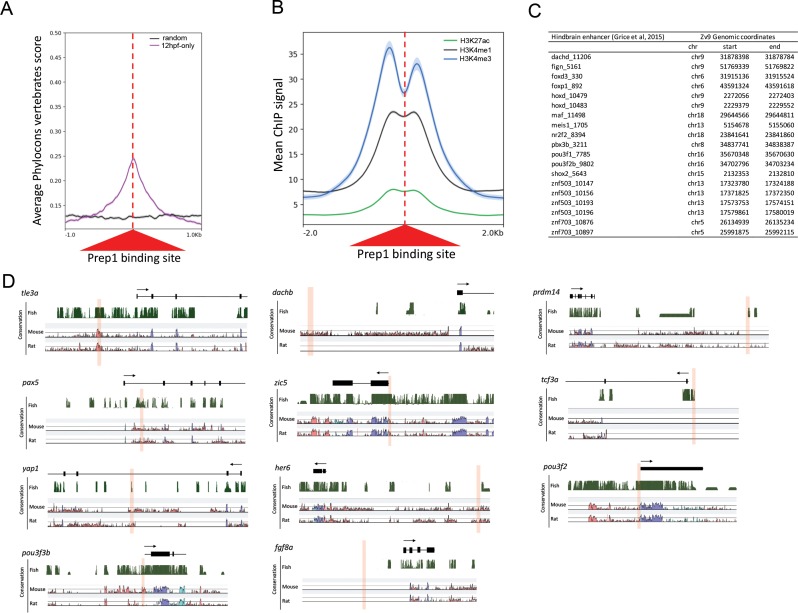
See also Figure 4—figure supplements 1 and 2. (A) Heatmaps displaying chromatin features at genomic regions occupied by Prep at 3.5hpf. H3K4me1 signals at Prep-occupied elements was analyzed by K-mean (k = 4) clustering (left panel). H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3, nucleosome, RNA-pol2 subunit RPB1 and Methyl CpG signals are displayed based on the H3K4me1 clustering order. (B) Average nucleosome signal at MPADs and non-MPADs (as defined in A). (C) Distribution of MPADs and non-MPADs relative to TSSs. (D) GO term enrichment for MPADs and non-MPADs identified by GREAT (nearest gene within 30 kb). Note that genes associated with Class 3 MPADs or non-MPADS are not enriched for GO terms. Only select categories are presented, a full list of GO terms is available in Supplementary file 2. FDR = Binomial False Discovery Rate. (E) Conservation of 3.5hpf Prep-occupied sites among vertebrates generated using PhastCons vertebrate 8-way comparison. The score shown is the probability (0 ≤ p ≤ 1) that each nucleotide belongs to a conserved genomic element. (F) Heatmaps displaying chromatin features at MPADs. H3K27ac and H3K27me3 signals at MPADs were analyzed by K-mean (k = 4) clustering. H3K4me1, H3K4me3, nucleosome and RBP1 signals are displayed based on the H3K27ac/me3 clustering order. (G) Box plots showing average expression of genes near (≤30 kb) each of the four MPAD classes, as determined by RNA-seq on 6hpf embryos. Data are presented as log2 of mean TPM (transcripts per million) values from three biological replicates. Statistical test: pairwise comparison with Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn's post-hoc test.