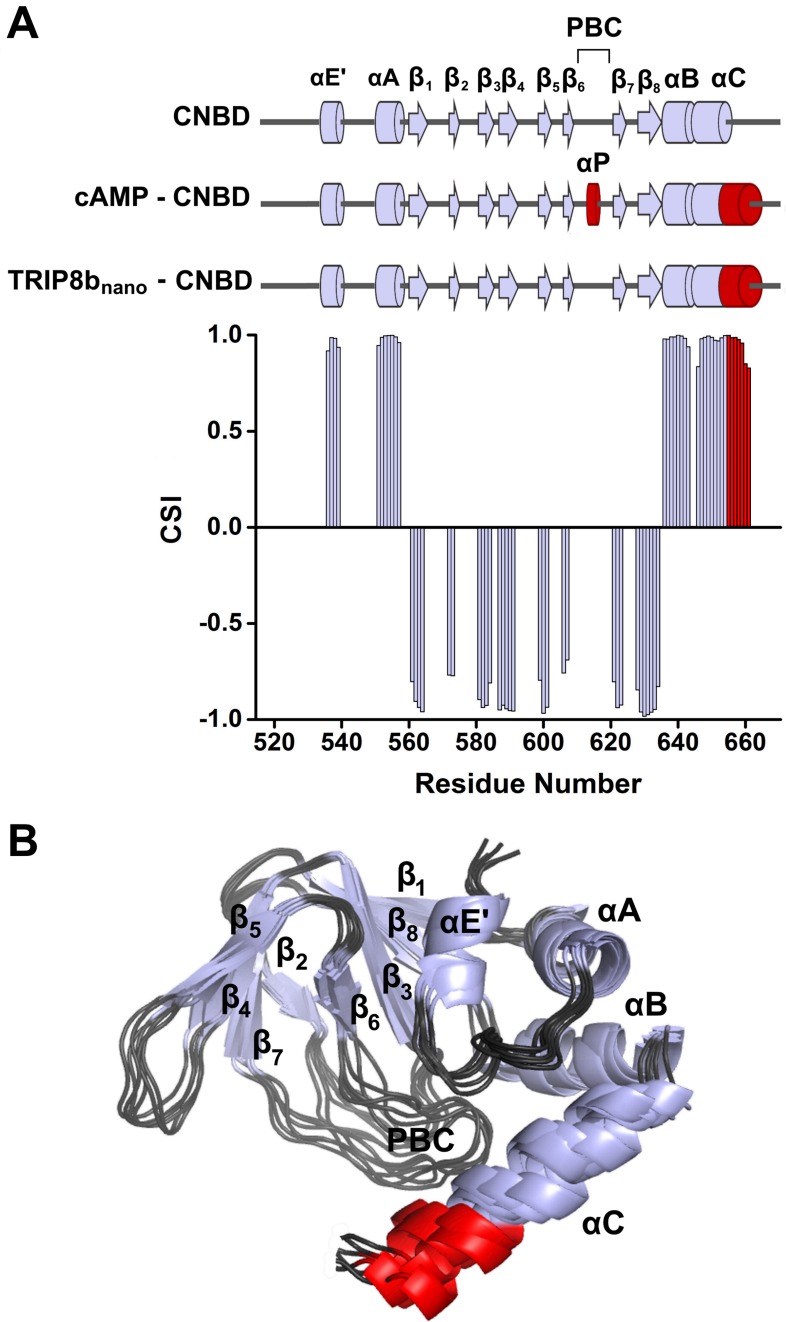
Figure 2. NMR structure of CNBD bound to TRIP8bnano.
(A) (Top) comparison of secondary structure elements of cAMP-free CNBD (Saponaro et al., 2014), cAMP-bound CNBD (Zagotta et al., 2003) and cAMP-free CNBD bound to TRIP8bnano (this study). Secondary structure elements are indicated by arrows (β-strands) and cylinders (α-helices) and labeled. The loop between β6 and β7 constitutes the Phosphate Binding Cassette (PBC). The elements that fold upon binding of cAMP and TRIP8bnano are shown in red. (Bottom) Chemical Shift Index (CSI, calculated using TALOS+) plotted as a function of the residue number of CNBD bound to TRIP8bnano. Positive values represent helical propensity, while negative values represent strands. (B) Ribbon representation of the 10 lowest energy conformers of CNBD bound to TRIP8bnano used for in silico modeling of CNBD - TRIP8bnano complex. Secondary structure elements are coloured in light gray and labeled. Loop regions are colored in dark gray. The distal region of the C-helix (residues 657–662), which is unfolded in the free form of the CNBD (Saponaro et al., 2014) and folds upon TRIP8bnano binding, is coloured in red. The unfolded regions at the N- and C-termini of the construct (residues 521–532 and 663–672 respectively) are omitted for clarity.