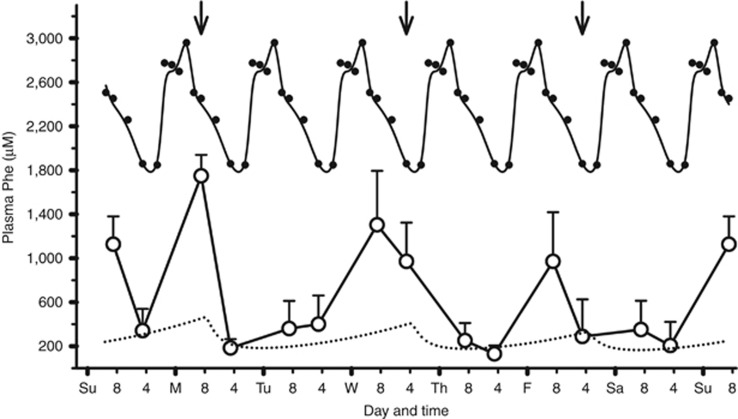
Figure 1.
Diurnal variation in plasma phenylalanine (Phe) levels of pegvaliase-treated phenylketonuria (PKU) mice. Twelve female PKU mice (Study 09-068a) were injected subcutaneously three times weekly with 10 mg/kg pegvaliase (Monday, 8 AM; Wednesday, 4 PM; Friday, 4 PM; ↓). Pharmocodynamic modeling of this dose schedule, (▪▪▪▪) predicted good regulation of plasma Phe levels. Blood samples (40 μl) were collected at 8 AM and 4 PM on different days of the week over a 7-week period and plasma Phe levels averaged to yield a composite weekly plasma Phe levels plot (○). The x-axis major hash marks represent days of the week (12 AM) and the minor hash marks indicate 8 AM and 4 PM. Composite data from untreated PKU female mice (Figure 2, •) were repeated seven times to show peak correspondence with the weekly plasma Phe data from pegvaliase treatment. Plasma Phe peaks occur in the treated animals at times corresponding to maximum plasma Phe levels in untreated PKU mice, although marked reduction of 8 AM plasma Phe values are seen on days after a pegvaliase dose was administered.