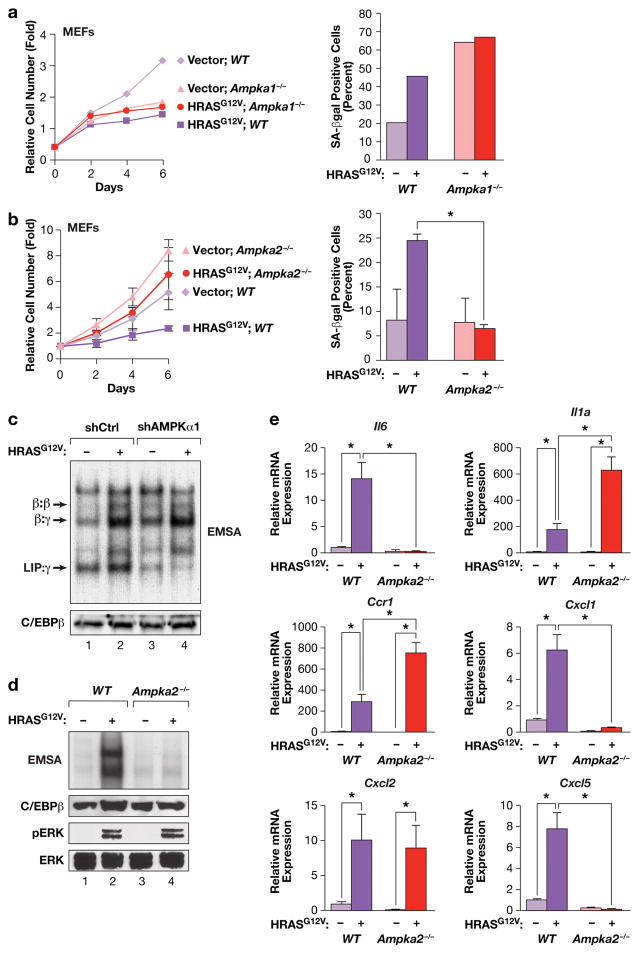
Figure 4.
HRASG12V-induced senescence and C/EBPβ activation in MEFs is dependent on AMPKα2. (a) RAS-induced growth arrest and senescence is independent of AMPKα1 but requires AMPKα2. WT and Ampka1−/− MEFs were infected with control or HRASG12V-expressing retroviruses, and cell proliferation (left panel) and senescence (SA-β-Gal staining, right panel) were analyzed. n=1 experiment. b) RAS-induced growth arrest and senescence requires AMPKα2. WT and Ampka2−/− MEFs were infected with control or HRASG12V-expressing retroviruses, and cell proliferation (left panel) and senescence (SA-β-Gal staining, right panel) were analyzed. n=3 experiments for growth curves (assayed in triplicate), n=2 for SA-β-Gal assays; error bars represent S.E.M. Statistical differences were determined by Student’s t test; *p<0.05. (c) C/EBPβ DNA binding is not affected by loss of AMPKα1. AMPKα1 was depleted in WT MEFs by shRNA knockdown, without or with expression of HRASG12V. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by EMSA using a canonical C/EBP site probe. (d) RAS-induced activation of C/EBPβ DNA binding is disrupted in Ampka2−/− MEFs. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by EMSA using a canonical C/EBP site probe. Levels of C/EBPβ, p-ERK and total ERK are also shown. (e) Analysis of SASP gene expression in WT and Ampka2−/− MEFs by qRT-PCR. n=2 biological replicates, each sample assayed in triplicate. Values are averages and error bars represent S.D. Statistical significance was calculated using Student’s two-tailed t test; *p<0.05.