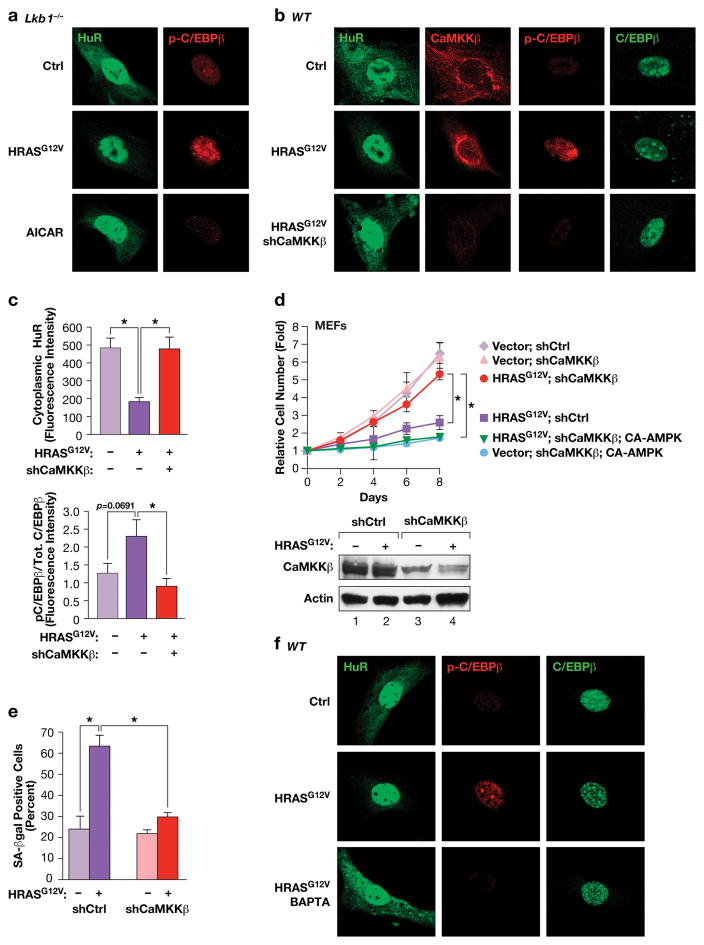
Figure 6.
The AMPK kinase CaMKKβ, but not LKB1, controls HRASG12V-induced nuclear translocation of HuR and C/EBPβ activation through a Ca++-dependent pathway. (a) IF staining of HuR and p-C/EBPβ in control and HRASG12V-expressing or AICAR-treated Lkb1−/− MEFs. (b) CaMKKβ depletion prevents HRASG12V-induced activation of the HuR-C/EBPβ pathway. WT MEFs expressing non-specific or shCaMKKβ hairpin RNAs, ± HRASG12V, were analyzed by IF staining for HuR, CaMKKβ, p-C/EBPβ (Thr188) and total C/EBPβ. (c) Quantification of cytoplasmic HuR and p-C/EBPβ:total C/EBPβ ratios from the experiment of panel (b). n=7 cells; error bars represent S.E.M. Statistical differences were determined by Student’s t test; *p<0.05. (d) Proliferation assays were performed using the cells described in panel (b) without or with expression of CA-AMPKα2. n=3; error bars represent S.E.M. Statistical differences at day 8 were determined by Student’s t test; *p<0.05. Lower panel: immunoblot confirming CaMKKβ depletion. (e) Effect of CaMKKβ depletion on RAS-induced senescence (SA-β-Gal positive cells). n=130 cells scored from two independent experiments; error bars represent S.E.M. Statistical differences were determined by Student’s t test; *p<0.05. (f) The Ca++ chelator, BAPTA, blocks HRASG12V-induced HuR nuclear translocation and C/EBPβ phosphorylation. Control and HRASG12V-expressing MEFs were treated with vehicle or 10 μM BAPTA for 2 hr prior to fixation. The cells were immunostained for the indicated proteins.