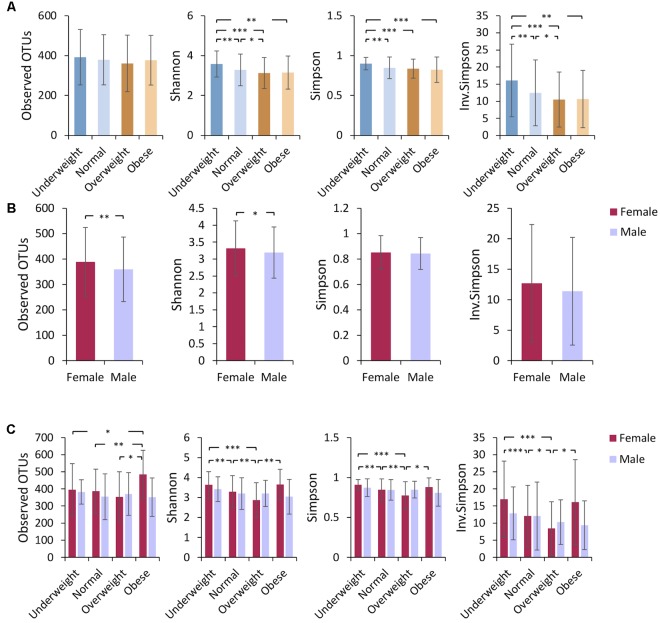
FIGURE 1.
Underweight individuals tend to have higher microbiome alpha diversity. Alpha diversity (mean ± standard deviation) was compared (A) among different BMI groups, (B) between females and males, and (C) among gender-specific BMI groups. Bacterial community richness was defined by the observed number of OTUs and alpha diversity was calculated using the Shannon index, Simpson index, and Inverse Simpson index. Paired t-tests were performed for alpha diversity measures. The P-value ranges are: ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.