Figure 3.
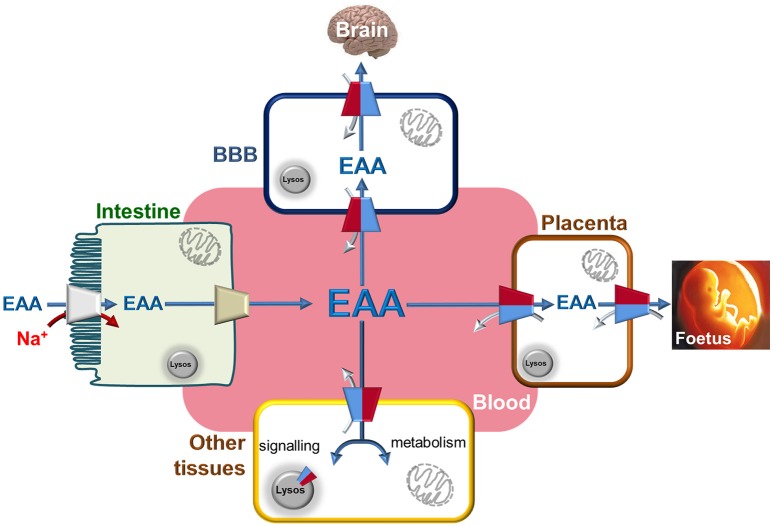
The Essential Amino Acids distribution network through LAT1. Interplay among blood and epithelial polarized cells of intestine (apical membrane depicted as brush-border and basolateral membrane in contact with blood), placenta, BBB (Blood Brain Barrier) and other tissues. Essential Amino Acids are absorbed through intestine using Na+ dependent transporters (indicated in gray) to allow their accumulation with high capacity. The same amino acids are conveyed to blood by other transporters present in the basolateral membrane of gut cells (indicated in light brown). From blood, Essential Amino Acids are accumulated in BBB and in placenta cells using LAT1 with an antiport reaction. In these cells, LAT1 is localized at both sides of cells allowing the flux of amino acids to Brain and Fetus, respectively. In other tissues, LAT1 is not highly expressed but plays the role of distributing Essential Amino Acids used both for signaling and metabolic purposes thanks also to alternative localization in lysosome membrane. These aspects became more important in tissues where LAT1 expression is strongly increased as in case of cancers. LAT1 is depicted as in Figure 2 by two-colored half. Flux of Essential Amino Acids are indicated by blue arrows (from blood to tissues) and by gray arrows (from tissues to blood).