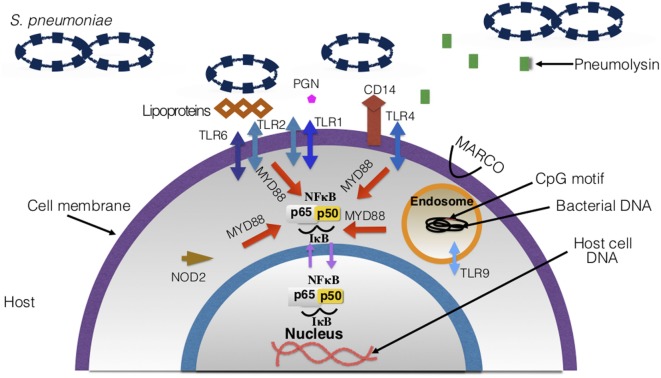
Figure 7.
Host surface and intracellular receptors necessary for immune response to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Highlighted in this figure are the major pathogen recognition receptors necessary for binding to pneumococcal ligands and eliciting an immune response. Upon binding to the ligands, receptors and signaling pathways are activated, which leads to the overall production of inflammatory cytokines and recruitment of immune cells. There are 10 toll-like receptors (TLRs) that have been discovered in humans—TLRs involved in pneumococcal disease are depicted in the figure.