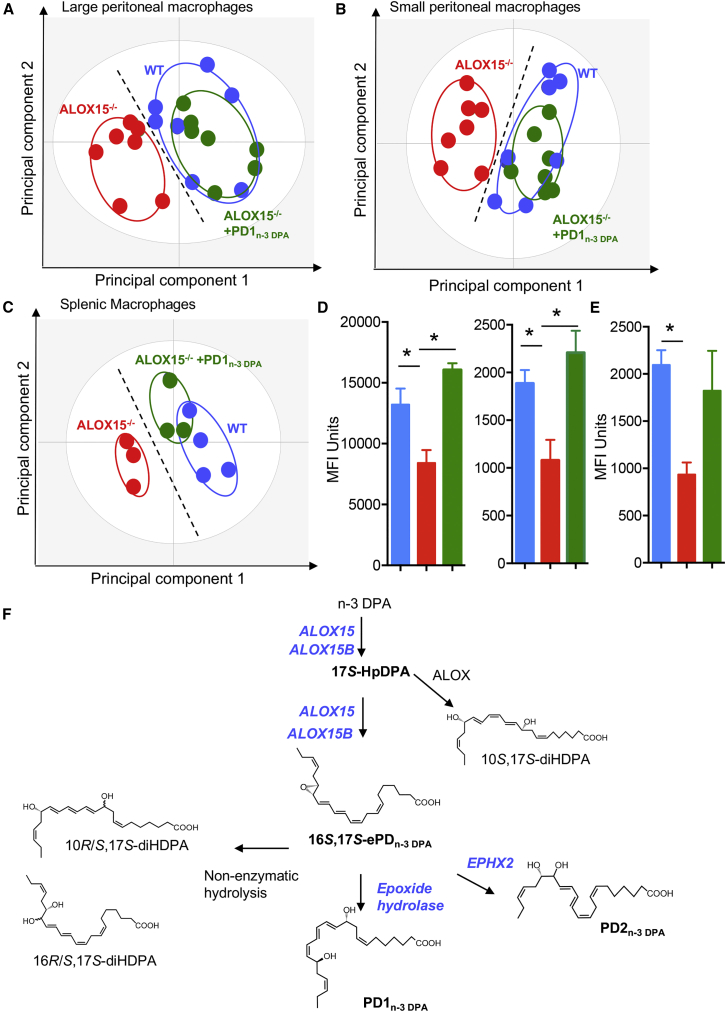
Figure 7.
PD1n-3 DPA Rectifies Murine Resident Macrophage Phenotype and Function in ALOX15-Deficient Mice
(A–C) The expression of phenotypic markers was assessed in peritoneal and splenic macrophages from ALOX15−/− mice administered PD1n-3 DPA (10 ng/mouse for 7 days) or vehicle and WT mice using flow cytometry and macrophage phenotype interrogated using PLS-DA in (A) large peritoneal macrophages, (B) small peritoneal macrophages, and (C) splenic macrophages. Results are representative of n = 8 mice per group for (A and B) and n = 3–4 mice per group for (C).
(D and E) Mice were treated as in (A–C), and on day 7 administered fluorescently labeled (D) apoptotic cells (6 × 106 cells/mouse) or (E) E. coli (106 CFU/mouse) via an intraperitoneal injection. Peritoneal cells were collected after 1 hr and phagocytosis was assessed in (D) CD64+ large peritoneal macrophages (left panel) and small peritoneal macrophages (right panel), and (E) total CD64+ macrophage population. Results are mean ± SEM. n = 8 mice per group for (D) and n = 4 mice per group for (E). *p < 0.05.
(F) Structures are illustrated in most likely configurations based on biosynthetic evidence. The stereochemistries for PD1n-3 DPA and 16S,17S-PDn-3 DPA are established (Aursnes et al., 2015, Aursnes et al., 2014, Dalli et al., 2013a).
Related to Figures S5.